Security Gateway as ICAP Server
Check Point ICAP Server![]() The ICAP Server functionality in your Security Gateway or Cluster (in versions R80.40 and higher) enables it to interact with an ICAP Client requests, send the files for inspection, and return the verdict. can work with multiple ICAP Clients.
The ICAP Server functionality in your Security Gateway or Cluster (in versions R80.40 and higher) enables it to interact with an ICAP Client requests, send the files for inspection, and return the verdict. can work with multiple ICAP Clients.
Check Point ICAP Server is supported only on Security Gateways R80.20 and higher, and supports only the Threat Emulation![]() Check Point Software Blade on a Security Gateway that monitors the behavior of files in a sandbox to determine whether or not they are malicious. Acronym: TE. and Anti-Virus
Check Point Software Blade on a Security Gateway that monitors the behavior of files in a sandbox to determine whether or not they are malicious. Acronym: TE. and Anti-Virus![]() Check Point Software Blade on a Security Gateway that uses real-time virus signatures and anomaly-based protections from ThreatCloud to detect and block malware at the Security Gateway before users are affected. Acronym: AV. blades. Any other blades in a Threat Prevention profile are ignored. If you enable ICAP Server on the gateway and not enable the Threat Emulation or the Anti-Virus blades, the ICAP Server runs but without inspection.
Check Point Software Blade on a Security Gateway that uses real-time virus signatures and anomaly-based protections from ThreatCloud to detect and block malware at the Security Gateway before users are affected. Acronym: AV. blades. Any other blades in a Threat Prevention profile are ignored. If you enable ICAP Server on the gateway and not enable the Threat Emulation or the Anti-Virus blades, the ICAP Server runs but without inspection.
The ICAP Server operates according to the relevant settings defined for Threat Emulation and Anti-Virus in the selected Threat Prevention profile and engine settings.
ICAP Server functionality is not supported in VSX![]() Virtual System Extension. Check Point virtual networking solution, hosted on a computer or cluster with virtual abstractions of Check Point Security Gateways and other network devices. These Virtual Devices provide the same functionality as their physical counterparts. mode and ClusterXL Load Sharing mode.
Virtual System Extension. Check Point virtual networking solution, hosted on a computer or cluster with virtual abstractions of Check Point Security Gateways and other network devices. These Virtual Devices provide the same functionality as their physical counterparts. mode and ClusterXL Load Sharing mode.
If you enable the ICAP Server on a Check Point Cluster![]() Two or more Security Gateways that work together in a redundant configuration - High Availability, or Load Sharing. object:
Two or more Security Gateways that work together in a redundant configuration - High Availability, or Load Sharing. object:
-
You must configure your ICAP Clients to communicate with the applicable Virtual IP Address of the Check Point Cluster.
-
ICAP connections do not survive cluster failover.
ICAP Server Actions
Check Point ICAP Server has 3 possible actions:
|
ICAP Action |
Description and Example |
|---|---|
|
Block |
For example: A Check Point UserCheck |
|
Continue / Not modified |
A default gateway or a proxy server can forward the HTTP Request / Response to its original destination. |
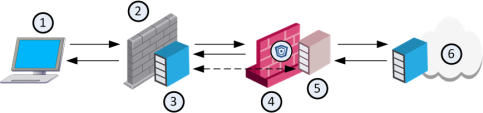
ICAP Server Sample Workflow
|
Step |
Instructions |
|---|---|
|
1 |
The client sends a request to the third party gateway/proxy server to download a file. |
|
2 |
The third party gateway/proxy sends the download request to the Web server. |
|
3 |
The Web server sends the requested file to the third party gateway/proxy. |
|
4 |
The ICAP Client forwards the file to the ICAP Server which is in the Check Point Threat Emulation gateway. |
|
5 |
The ICAP Server sends the file to the Threat Emulation engine. |
|
6 |
The Threat Emulation checks the file
|
Configuring ICAP Server for Threat Prevention
You can create a new ICAP service and select it instead of the default service.
|
Step |
Instructions |
|---|---|
|
1 |
Go to the objects bar and select New > More > Service > TCP. |
|
2 |
Enter the object name and add a comment if necessary. |
|
3 |
In General, do not select a protocol. |
|
4 |
In Match By, select the Port you want the service to run on. |
|
5 |
Optional: Configure the Advanced features. For a detailed explanation on the advanced service features, check the online help. |
|
6 |
Click OK. |
The new service now appears in the drop-down Service list.
When you enable ICAP Server on the gateway object, an auto-generated rule is created in the Threat Prevention Rule Base![]() All rules configured in a given Security Policy. Synonym: Rulebase.. One rule is created for each gateway that has ICAP Server enabled. You can only configure the profile column in this rule. You can select a different profile for each ICAP rule. Unlike other Threat Prevention rules, you cannot create exceptions for an ICAP rule.
All rules configured in a given Security Policy. Synonym: Rulebase.. One rule is created for each gateway that has ICAP Server enabled. You can only configure the profile column in this rule. You can select a different profile for each ICAP rule. Unlike other Threat Prevention rules, you cannot create exceptions for an ICAP rule.
|
|
Note - ICAP Server supports only Anti-Virus deep-scan. Any additional functionality, such as MD5 hash, URL reputation, and signature-based protection, is not supported. |
For information on how to test ICAP Server functionality, see sk174487.
Advanced ICAP Server Configuration on the Security Gateway
The ICAP Server) uses processes to handle the requests it receives from the ICAP Client. Each process generates multiple threads, and each thread handles one request from the ICAP Client to the ICAP Server.
The ICAP Server supports dynamic scaling of the number of processes for optimal performance. The number of available threads increases or decreases as needed. The minimum number of processes is three.
-
The maximum allowed number of server processes is configured on the Security Gateway. In addition, you can configure The number of threads per a child process.
-
The maximum allowed number of server processes multiplied by The number of threads per a child process is the number of maximum concurrent connections that the ICAP Server can handle.
-
Start a new child process if the number of available threads is less than [x] - This option allows dynamic growth and lets you configure the number of new threads as needed. The ICAP Server counts the total number of available (idle) threads. If this number is lower than the number configured in this field, it creates a new child process.
-
End a child process if the number of available threads is more than [x] - This option allows dynamic reduction of the number of threads as needed. The ICAP Server counts the total number of available (idle) threads. If this number is higher than the number configured in this field, it ends a child process.
Threat Prevention Settings and ICAP Server
The ICAP Server operates according to the relevant settings defined for Threat Emulation and Anti-Virus in the selected Threat Prevention profile and engine settings.
Emulation Connection Handling Mode and ICAP Server
In the Threat Prevention default profiles (Basic, Optimized, and Strict), Threat Emulation is set to Rapid Delivery mode.
Rapid Delivery mode means that connections are allowed until emulation is complete.
In Maximum Prevention mode, the connections are blocked until emulation is complete. You can create a new profile and change the mode to Maximum Prevention mode, and apply the profile to the relevant gateways.
Related Configuration on the ICAP Client
When you work with Check Point ICAP Server, make sure to set this configuration on your ICAP Client.
-
Direct the ICAP modification requests to the ICAP Server sandblast service.
For example:
icap://<IP_Address>:1344/sandblast -
Set the ICAP Client to send these headers, if possible:
X-Client-IPX-Server-IPX-Authentication-User
These headers are used in the ICAP Server logs.
-
Make sure the operation timeout for the ICAP Client is equal or higher than the operation timeout for the ICAP Server.
Note - The sandblast service on the Check Point ICAP Server can take some time to respond.
-
For HTTPS traffic, configure the ICAP Client to send clear HTTP (decrypted HTTPS) traffic to the Check Point ICAP Server. If this option is not available on your ICAP Client, the ICAP Server is not able to process the traffic.
|
|
Notes:
|
Use Case
You can use the ICAP technology to communicate HTTPS content.
You are a system administrator, who manages a network that includes a third party gateway/proxy and a Check Point Security Gateway.
The Check Point Security Gateway enforces the Threat Emulation and Anti-Virus blades.
The third party gateway/proxy has HTTPS Inspection![]() Feature on a Security Gateway that inspects traffic encrypted by the Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) protocol for malware or suspicious patterns. Synonym: SSL Inspection. Acronyms: HTTPSI, HTTPSi. enabled, but the Check Point Security Gateway does not.
Feature on a Security Gateway that inspects traffic encrypted by the Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) protocol for malware or suspicious patterns. Synonym: SSL Inspection. Acronyms: HTTPSI, HTTPSi. enabled, but the Check Point Security Gateway does not.
With the ICAP Client and Check Point ICAP Server enabled and configured to work together, the ICAP Client can send the decrypted traffic to the ICAP Server for inspection. This way, the Check Point Security Gateway can read the HTTPS content for the Threat Emulation and Anti-Virus blades, even if no HTTPS Inspection is enabled on the Check Point Security Gateway.
|
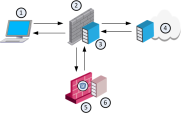
Item No. |
Description |
|---|---|
|
1 |
HTTPS client |
|
2 |
Third party gateway or proxy |
|
3 |
ICAP Client |
|
4 |
Check Point Security Gateway |
|
5 |
Check Point ICAP Server |
|
6 |
Web server |
Workflow:
|
Step |
Instructions |
|---|---|
|
1 |
The HTTPS client initiates an HTTPS connection, which is sent to the proxy server. |
|
2 |
Proxy server forwards the HTTPS connection to the Check Point Security Gateway. |
|
3 |
The Check Point Security Gateway forwards the HTTPS connection to the web server. |
|
4 |
The web server sends the requested data over HTTPS to the Check Point Security Gateway. |
|
5 |
The Check Point Security Gateway forwards the HTTPS connection to the proxy server. |
|
6 |
The ICAP Client decrypts the HTTPS connection (the ICAP Client is configured to work in RESPMOD). |
|
7 |
The ICAP Client sends the decrypted HTTPS content to the ICAP Server for a verdict. |
|
8 |
The ICAP Server returns a verdict to the ICAP Client. |
|
9 |
Based on the verdict, the proxy server allows or blocks the requested HTTPS data. |