What's New
Introduction
As our networks continue to increase and the threat landscape continues to evolve, customers need security solutions that allow endless scalability and simple operations. With over 100 new features, R80.40, is imperative for putting our network security on the fast track. Providing unified management for both physical and virtual networks, on premise, and cloud enforcement points. By consolidating all aspects of your security environment seamlessly, it allows you to deploy protections across your organization without impeding business innovation. It also allows full visibility into security across your network in a customizable visual dashboard, helping you monitor and focus on what matters to you. With its scalable, extensible architecture, you can manage the most complex environments easily and efficiently.
This release contains innovations and significant improvements such as:
-
SmartTasks - automate daily work with predefined or customizable actions.
-
Dedicated HTTPS policy layer - prevents encrypted traffic from Gen V attacks.
-
Zero-touch deployment – decreases the deployment time from hours to minutes for installing new gateways.
-
IoT Security Manager - manages Identify IoT devices and seamlessly turns their attributes into an IoT security policy
 Collection of rules that control network traffic and enforce organization guidelines for data protection and access to resources with packet inspection..
Collection of rules that control network traffic and enforce organization guidelines for data protection and access to resources with packet inspection..
New in this release
IoT Security
A new IoT security controller to:
-
Collect IoT devices and traffic attributes from certified IoT discovery engines (currently supports Medigate, CyberMDX, Cynerio, Claroty, Indegy, SAM, and Armis).
-
Configure a new IoT dedicated Policy Layer
 Layer (set of rules) in a Security Policy. in policy management.
Layer (set of rules) in a Security Policy. in policy management. -
Configure and manage security rules that are based on the IoT devices attributes.
HTTPS Inspection
HTTP/2
HTTP/2 is an update to the HTTP protocol. The update provides improvements to speed, efficiency and security and results with a better user experience.
-
Check Point Security Gateway
 Dedicated Check Point server that runs Check Point software to inspect traffic and enforce Security Policies for connected network resources. now supports HTTP/2 and benefits better speed and efficiency while getting full security, with all Threat Prevention and Access Control Software Blades, as well as new protections for the HTTP/2 protocol.
Dedicated Check Point server that runs Check Point software to inspect traffic and enforce Security Policies for connected network resources. now supports HTTP/2 and benefits better speed and efficiency while getting full security, with all Threat Prevention and Access Control Software Blades, as well as new protections for the HTTP/2 protocol. -
Support is for both clear and SSL encrypted traffic and is fully integrated with HTTPS Inspection
 Feature on a Security Gateway that inspects traffic encrypted by the Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) protocol for malware or suspicious patterns. Synonym: SSL Inspection. Acronyms: HTTPSI, HTTPSi. capabilities.
Feature on a Security Gateway that inspects traffic encrypted by the Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) protocol for malware or suspicious patterns. Synonym: SSL Inspection. Acronyms: HTTPSI, HTTPSi. capabilities.
HTTPS Inspection Layer
Provides these new capabilities:
-
A new Policy Layer in SmartConsole
 Check Point GUI application used to manage a Check Point environment - configure Security Policies, configure devices, monitor products and events, install updates, and so on. dedicated to HTTPS Inspection.
Check Point GUI application used to manage a Check Point environment - configure Security Policies, configure devices, monitor products and events, install updates, and so on. dedicated to HTTPS Inspection. -
Different HTTPS Inspection layers can be used in different policy packages.
-
Sharing of a HTTPS Inspection layer across multiple policy packages.
-
API for HTTPS Inspection operations.
Threat Prevention
Optimized Security and Productivity for the Different Modes – Threat Extraction![]() Check Point Software Blade on a Security Gateway that removes malicious content from files. Acronym: TEX. works with Threat Emulation
Check Point Software Blade on a Security Gateway that removes malicious content from files. Acronym: TEX. works with Threat Emulation![]() Check Point Software Blade on a Security Gateway that monitors the behavior of files in a sandbox to determine whether or not they are malicious. Acronym: TE. to provide users with more productivity without compromising security.
Check Point Software Blade on a Security Gateway that monitors the behavior of files in a sandbox to determine whether or not they are malicious. Acronym: TE. to provide users with more productivity without compromising security.
Background Mode is now called Rapid Delivery to prevent many more malicious files within the emulation window of 3 seconds.
Hold Mode is now called Maximum Prevention and provides improved productivity to ensure that all Threat Extraction cleaned documents deliver quickly to end users. Maximum Security minimizes the time users wait without a compromise on security.
To learn more, see the R80.40 Threat Prevention Administration Guide > Chapter Advanced Threat Emulation Settings.
Threat Extraction
Automatic Engine Updates – Like the automatic updates to the Threat Emulation engines, you can now receive Threat Extraction updates automatically on your gateways. There is no need to update to a hotfix![]() Software package installed on top of the current software version to fix a wrong or undesired behavior, and to add a new behavior. or a major version. Security improvements, new features and more do not require intervention.
Software package installed on top of the current software version to fix a wrong or undesired behavior, and to add a new behavior. or a major version. Security improvements, new features and more do not require intervention.
Anti-Virus and SandBlast Threat Emulation
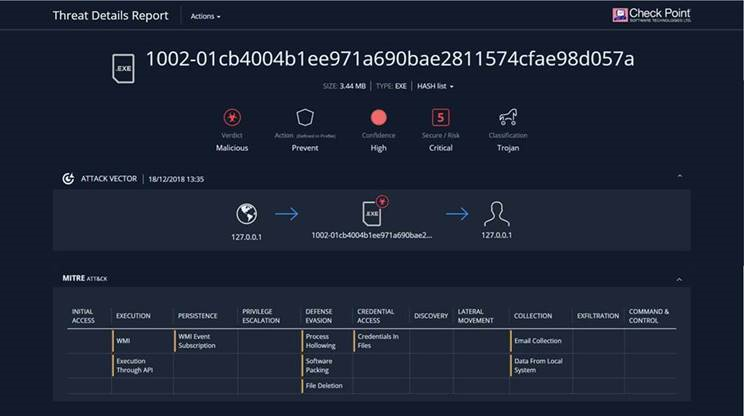
MITRE ATT&CK™ Reporting – Threat Emulation Forensics Reports now include a detailed MITRE ATT&CK Matrix with the detected adversary tactics and techniques for every malicious executable file.
Enhanced Support for Archive Files – includes significant improvements in handling archive files:
-
Support for password protection for all supported file types, including
*.7zand*.rar. For more details, see sk112821. -
An improved mechanism to “guess” passwords automatically when it opens password-protected archives for emulation.
-
Added support for password-protected archives when the password includes Unicode characters.
-
Stability improvements.
Faster delivery of an emulation verdict for documents with embedded files.
Enhanced Support for Password-Protected Documents:
- Admins can now configure a default action for password-protected documents. If such a file is emulated, the file is allowed or blocked by default. To configure a default action, follow the instructions in sk132492.
New File Types and Protocols:
-
Attachments from Nested MSG Files - Threat Emulation now supports emulation for files that attach to MSG files that attach to other MSG files.
-
Support for new Archive Formats - WIM, CHM, CramFS, DMG, EXT, FAT, GPT, HFS, IHEX, MBR, MSI, NSIS, NTFS, QCOW2, RPM, SquashFS, UDF, UEFI, VDI, VHD, VMDK, LZH, ARJ, CPIO, AR.
-
SCP and SFTP file transfers can be scanned using SSH Deep Packet Inspection.
-
SMBV3 Multi-Channel Connections – Multi-channel file transfer is on by default on all Windows operating systems. The Check Point Security Gateway is now the only one in the market that inspects large file transfers through SMBv3 (3.0, 3.0.2, 3.1.1) over multi-channel connections.
Enhanced Logging for Emulated Archive Files:
-
The archive file log includes the names of all the files inside.
-
A new log generates for every extracted file from the archive with its emulation results. This log contains the name of the archive file. Logs correlate easily between the archive file and those of the files it contains.
Importing SHA-256 IoC![]() Indicator of Compromise. Artifact observed on a network or in an operating system that, with high confidence, indicates a computer intrusion. Typical IoCs are virus signatures and IP addresses, MD5 hashes of Malware files, or URLs or domain names of botnet command and control servers. Identified through a process of incident response and computer forensics, intrusion detection systems and anti-virus software can use IoC's to detect future attacks. feeds - Anti-Virus
Indicator of Compromise. Artifact observed on a network or in an operating system that, with high confidence, indicates a computer intrusion. Typical IoCs are virus signatures and IP addresses, MD5 hashes of Malware files, or URLs or domain names of botnet command and control servers. Identified through a process of incident response and computer forensics, intrusion detection systems and anti-virus software can use IoC's to detect future attacks. feeds - Anti-Virus![]() Check Point Software Blade on a Security Gateway that uses real-time virus signatures and anomaly-based protections from ThreatCloud to detect and block malware at the Security Gateway before users are affected. Acronym: AV. now supports SHA-256 hashes as Indicators of Compromise (IoC). Administrators can import SHA-256 IoC feeds manually or connect the Security Gateway to a live feed of SHA-256 IoC. For more information, see sk132193.
Check Point Software Blade on a Security Gateway that uses real-time virus signatures and anomaly-based protections from ThreatCloud to detect and block malware at the Security Gateway before users are affected. Acronym: AV. now supports SHA-256 hashes as Indicators of Compromise (IoC). Administrators can import SHA-256 IoC feeds manually or connect the Security Gateway to a live feed of SHA-256 IoC. For more information, see sk132193.
Replacing the Threat Emulation API Certificate – Administrators can now upload their own certificate to use for Threat Emulation API calls to their Threat Emulation Appliance. For more information, see sk160693.
Email Security
-
Enhanced Support for POP3 and IMAP protocols - Anti-Virus and SandBlast Threat Emulation now support inspection of e-mail over the POP3 protocol and improve inspection of e-mail over the IMAP protocol.
-
Enhanced Protection against BaseStriker - MTA Gateways now protect against malicious emails with URLs that use the BaseStriker technique.
-
Bounce Messages Behavior Change - Modifies the configuration of the MTA so that it tries to send bounce messages only once whether it reaches its destination or not.
-
Enhanced Threat Emulation inspection for files behind shortened links - The body of an email sometimes includes customized Bitly links that point to files. With this release, Threat Emulation scans the files behind these links to detect zero-day attacks. This capability requires Threat Emulation and Anti-Virus to be enabled and MTA must be configure for the Security Gateway.
[Early Availability] Click-Time URL Protection – The MTA Security Gateway can now re-write links in incoming emails. When users click on them, the resources (web sites or files) behind the links have inspections again. This prevents delayed attacks where attackers replace the resource behind the link after the email delivery.
[Early Availability] Anti-Phishing Engine – The MTA Security Gateway introduces a new state of the art Anti-Phishing engine. This design alerts against and prevents sophisticated phishing, spear phishing, and targeted phishing attacks.
Want to join the program and hear more? Contact us at email_security@checkpoint.com.
Other Enhancements
Dynamic, Domain and Updatable Objects can be used in Threat Prevention and HTTPS Inspection Policies.
Domain objects enchantment - DNS passive learning. For more information, see sk161612.
Access Control
Identity Awareness
-
Support for Captive Portal
 A Check Point Identity Awareness web portal, to which users connect with their web browser to log in and authenticate, when using Browser-Based Authentication. integration with SAML 2.0 and third party Identity Providers.
A Check Point Identity Awareness web portal, to which users connect with their web browser to log in and authenticate, when using Browser-Based Authentication. integration with SAML 2.0 and third party Identity Providers. -
Support for Identity Broker
 Identity Sharing mechanism between Identity Servers (PDP): (1) Communication channel between PDPs based on Web-API (2) Identity Sharing capabilities between PDPs - ability to add, remove, and update the identity session. for scalable and granular sharing of identity information between PDPs, as well as cross-domain sharing.
Identity Sharing mechanism between Identity Servers (PDP): (1) Communication channel between PDPs based on Web-API (2) Identity Sharing capabilities between PDPs - ability to add, remove, and update the identity session. for scalable and granular sharing of identity information between PDPs, as well as cross-domain sharing. -
Enhancements to Terminal Servers Agent for better scaling and compatibility.
IPsec VPN
-
Configure different VPN encryption domains on a Security Gateway that is a member of multiple VPN communities. This provides:
-
Improved privacy - Internal networks are not disclosed in IKE protocol negotiations.
-
Improved security and granularity - Specify which networks are accessible in a specified VPN community.
-
Improved interoperability - Simplified route-based VPN definitions (recommended when you work with an empty VPN encryption domain).
-
-
Large Scale VPN (LSV) environment. Using LSV profiles provides the ability to connect Externally Managed and Third Party VPN peers seamlessly by simply providing them with the same CA certificate used by central Security Gateway.
Application Control
Improved performance, diagnostics and monitoring tools.
NAT
-
Enhanced NAT port allocation mechanism - on Security Gateways with 6 or more CoreXL
 Performance-enhancing technology for Security Gateways on multi-core processing platforms. Multiple Check Point Firewall instances are running in parallel on multiple CPU cores. Firewall instances, all instances use the same pool of NAT ports, which optimizes the port utilization and reuse.
Performance-enhancing technology for Security Gateways on multi-core processing platforms. Multiple Check Point Firewall instances are running in parallel on multiple CPU cores. Firewall instances, all instances use the same pool of NAT ports, which optimizes the port utilization and reuse. -
NAT port utilization monitoring in CPView and with SNMP.
Voice over IP (VoIP)
Multiple CoreXL Firewall instances handle the SIP protocol to enhance performance.
Remote Access VPN
Machine Certificate Authentication - use machine certificate to distinguish between corporate and non-corporate assets adding the ability to restrict access to corporate assets only. Enforcement can be pre-logon (device authentication only) or post-logon (device and user authentication).
Mobile Access Portal Agent
Enhanced Endpoint Security on Demand within the Mobile Access![]() Check Point Software Blade on a Security Gateway that provides a Remote Access VPN access for managed and unmanaged clients. Acronym: MAB. Portal Agent to support all major web browsers. For more information, see sk113410.
Check Point Software Blade on a Security Gateway that provides a Remote Access VPN access for managed and unmanaged clients. Acronym: MAB. Portal Agent to support all major web browsers. For more information, see sk113410.
Mobile Access
SMB v2/v3 mount support in Mobile Access Software Blade![]() Specific security solution (module): (1) On a Security Gateway, each Software Blade inspects specific characteristics of the traffic (2) On a Management Server, each Software Blade enables different management capabilities..
Specific security solution (module): (1) On a Security Gateway, each Software Blade inspects specific characteristics of the traffic (2) On a Management Server, each Software Blade enables different management capabilities..
Security Gateway and Gaia
CoreXL and Multi-Queue
-
Security Gateway automatically changes the number of CoreXL SNDs and Firewall instances and the Multi-Queue
 An acceleration feature on Security Gateway that configures more than one traffic queue for each network interface. Multi-Queue assigns more than one receive packet queue (RX Queue) and more than one transmit packet queue (TX Queue) to an interface. Multi-Queue is applicable only if SecureXL is enabled (this is the default). Acronym: MQ. configuration based on the current traffic load. For more information, see the R80.40 Performance Tuning Administration Guide.
An acceleration feature on Security Gateway that configures more than one traffic queue for each network interface. Multi-Queue assigns more than one receive packet queue (RX Queue) and more than one transmit packet queue (TX Queue) to an interface. Multi-Queue is applicable only if SecureXL is enabled (this is the default). Acronym: MQ. configuration based on the current traffic load. For more information, see the R80.40 Performance Tuning Administration Guide. -
Priority Queues are enabled by default. For more information, see sk105762.
Clustering
-
Multi-Version Clustering (MVC) – ClusterXL
 Cluster of Check Point Security Gateways that work together in a redundant configuration. The ClusterXL both handles the traffic and performs State Synchronization. These Check Point Security Gateways are installed on Gaia OS: (1) ClusterXL supports up to 5 Cluster Members, (2) VRRP Cluster supports up to 2 Cluster Members, (3) VSX VSLS cluster supports up to 13 Cluster Members. Note: In ClusterXL Load Sharing mode, configuring more than 4 Cluster Members significantly decreases the cluster performance due to amount of Delta Sync traffic. acts like a standard cluster
Cluster of Check Point Security Gateways that work together in a redundant configuration. The ClusterXL both handles the traffic and performs State Synchronization. These Check Point Security Gateways are installed on Gaia OS: (1) ClusterXL supports up to 5 Cluster Members, (2) VRRP Cluster supports up to 2 Cluster Members, (3) VSX VSLS cluster supports up to 13 Cluster Members. Note: In ClusterXL Load Sharing mode, configuring more than 4 Cluster Members significantly decreases the cluster performance due to amount of Delta Sync traffic. acts like a standard cluster Two or more Security Gateways that work together in a redundant configuration - High Availability, or Load Sharing. running cluster members with different software versions during upgrade scenarios supporting redundancy between members and state synchronization
Two or more Security Gateways that work together in a redundant configuration - High Availability, or Load Sharing. running cluster members with different software versions during upgrade scenarios supporting redundancy between members and state synchronization Technology that synchronizes the relevant information about the current connections (stored in various kernel tables on Check Point Security Gateways) among all Cluster Members over Synchronization Network. Due to State Synchronization, the current connections are not cut off during cluster failover..
Technology that synchronizes the relevant information about the current connections (stored in various kernel tables on Check Point Security Gateways) among all Cluster Members over Synchronization Network. Due to State Synchronization, the current connections are not cut off during cluster failover.. -
New ClusterXL mode: Active-Active
 A cluster mode (in versions R80.40 and higher), where cluster members are located in different geographical areas (different sites, different cloud availability zones). This mode supports the configuration of IP addresses from different subnets on all cluster interfaces, including the Sync interfaces. Each cluster member inspects all traffic routed to it and synchronizes the recorded connections to its peer cluster members. The traffic is not balanced between the cluster members.,supports running several cluster members in ACTIVE
A cluster mode (in versions R80.40 and higher), where cluster members are located in different geographical areas (different sites, different cloud availability zones). This mode supports the configuration of IP addresses from different subnets on all cluster interfaces, including the Sync interfaces. Each cluster member inspects all traffic routed to it and synchronizes the recorded connections to its peer cluster members. The traffic is not balanced between the cluster members.,supports running several cluster members in ACTIVE State of a Cluster Member that is fully operational: (1) In ClusterXL, this applies to the state of the Security Gateway component (2) In 3rd-party / OPSEC cluster, this applies to the state of the cluster State Synchronization mechanism. state, each member is a part of a separated routing domain and handles its own traffic, redundancy is kept during failover
State of a Cluster Member that is fully operational: (1) In ClusterXL, this applies to the state of the Security Gateway component (2) In 3rd-party / OPSEC cluster, this applies to the state of the cluster State Synchronization mechanism. state, each member is a part of a separated routing domain and handles its own traffic, redundancy is kept during failover Transferring of a control over traffic (packet filtering) from a Cluster Member that suffered a failure to another Cluster Member (based on internal cluster algorithms). Synonym: Fail-over..
Transferring of a control over traffic (packet filtering) from a Cluster Member that suffered a failure to another Cluster Member (based on internal cluster algorithms). Synonym: Fail-over.. -
Geo-Clustering in the Active-Active mode – Supports the configuration of the cluster Sync interface
 An interface on a Cluster Member, whose Network Type was set as Sync or Cluster+Sync in SmartConsole in cluster object. This interface is monitored by cluster, and failure on this interface will cause cluster failover. This interface is used for State Synchronization between Cluster Members. The use of more than one Sync Interfaces for redundancy is not supported because the CPU load will increase significantly due to duplicate tasks performed by all configured Synchronization Networks. Synonyms: Secured Interface, Trusted Interface. on different subnets while allowing L3 communication between the members on the sync interface. making the requirement for L2 connectivity and a trusted network between the cluster members (while working in Active-Active mode) obsolete.
An interface on a Cluster Member, whose Network Type was set as Sync or Cluster+Sync in SmartConsole in cluster object. This interface is monitored by cluster, and failure on this interface will cause cluster failover. This interface is used for State Synchronization between Cluster Members. The use of more than one Sync Interfaces for redundancy is not supported because the CPU load will increase significantly due to duplicate tasks performed by all configured Synchronization Networks. Synonyms: Secured Interface, Trusted Interface. on different subnets while allowing L3 communication between the members on the sync interface. making the requirement for L2 connectivity and a trusted network between the cluster members (while working in Active-Active mode) obsolete. -
Support for Cluster Control Protocol
 Proprietary Check Point protocol that runs between Cluster Members on UDP port 8116, and has the following roles: (1) State Synchronization (Delta Sync), (2) Health checks (state of Cluster Members and of cluster interfaces): Health-status Reports, Cluster-member Probing, State-change Commands, Querying for cluster membership. Note: CCP is located between the Check Point Firewall kernel and the network interface (therefore, only TCPdump should be used for capturing this traffic). Acronym: CCP. (CCP) in Unicast mode for any number of cluster members eliminating the need for CCP Broadcast, Multicast, or Automatic modes.
Proprietary Check Point protocol that runs between Cluster Members on UDP port 8116, and has the following roles: (1) State Synchronization (Delta Sync), (2) Health checks (state of Cluster Members and of cluster interfaces): Health-status Reports, Cluster-member Probing, State-change Commands, Querying for cluster membership. Note: CCP is located between the Check Point Firewall kernel and the network interface (therefore, only TCPdump should be used for capturing this traffic). Acronym: CCP. (CCP) in Unicast mode for any number of cluster members eliminating the need for CCP Broadcast, Multicast, or Automatic modes. -
Configuring VMAC
 Virtual MAC Address. When this feature is enabled in a ClusterXL (in the High Availability or Load Sharing Unicast mode), the current Active or Pivot Cluster Member sends Gratuitous ARP Requests (G-ARP) for its Cluster Virtual IP (VIP) addresses and Virtual MAC (VMAC) addresses in G-ARP updates. Cluster Members create a VMAC address for each Cluster VIP address. This feature helps avoid issues during a cluster failover, when switches do not integrate G-ARP updates into their ARP cache table. does not require changing the NIC to promiscuous mode.
Virtual MAC Address. When this feature is enabled in a ClusterXL (in the High Availability or Load Sharing Unicast mode), the current Active or Pivot Cluster Member sends Gratuitous ARP Requests (G-ARP) for its Cluster Virtual IP (VIP) addresses and Virtual MAC (VMAC) addresses in G-ARP updates. Cluster Members create a VMAC address for each Cluster VIP address. This feature helps avoid issues during a cluster failover, when switches do not integrate G-ARP updates into their ARP cache table. does not require changing the NIC to promiscuous mode. -
Eliminated the need for MAC Magic configuration when several clusters are connected to the same subnet.
-
Cluster Control Protocol (CCP) Encryption is now enabled by default.
VSX
-
Support for VSX
 Virtual System Extension. Check Point virtual networking solution, hosted on a computer or cluster with virtual abstractions of Check Point Security Gateways and other network devices. These Virtual Devices provide the same functionality as their physical counterparts. upgrade with CPUSE
Virtual System Extension. Check Point virtual networking solution, hosted on a computer or cluster with virtual abstractions of Check Point Security Gateways and other network devices. These Virtual Devices provide the same functionality as their physical counterparts. upgrade with CPUSE Check Point Upgrade Service Engine for Gaia Operating System. With CPUSE, you can automatically update Check Point products for the Gaia OS, and the Gaia OS itself. in Gaia Portal
Check Point Upgrade Service Engine for Gaia Operating System. With CPUSE, you can automatically update Check Point products for the Gaia OS, and the Gaia OS itself. in Gaia Portal Web interface for the Check Point Gaia operating system..
Web interface for the Check Point Gaia operating system.. -
Support for "Active Up
 ClusterXL in High Availability mode that was configured as Maintain current active Cluster Member in the cluster object in SmartConsole: (1) If the current Active member fails for some reason, or is rebooted (for example, Member_A), then failover occurs between Cluster Members - another Standby member will be promoted to be Active (for example, Member_B). (2) When former Active member (Member_A) recovers from a failure, or boots, the former Standby member (Member_B) will remain to be in Active state (and Member_A will assume the Standby state)." mode in Virtual System Load Sharing
ClusterXL in High Availability mode that was configured as Maintain current active Cluster Member in the cluster object in SmartConsole: (1) If the current Active member fails for some reason, or is rebooted (for example, Member_A), then failover occurs between Cluster Members - another Standby member will be promoted to be Active (for example, Member_B). (2) When former Active member (Member_A) recovers from a failure, or boots, the former Standby member (Member_B) will remain to be in Active state (and Member_A will assume the Standby state)." mode in Virtual System Load Sharing VSX Cluster technology that assigns Virtual System traffic to different Active Cluster Members. Acronym: VSLS. (VSLS).
VSX Cluster technology that assigns Virtual System traffic to different Active Cluster Members. Acronym: VSLS. (VSLS). -
Support for CPView statistical reports for each Virtual System
 Virtual Device on a VSX Gateway or VSX Cluster Member that implements the functionality of a Security Gateway. Acronym: VS.
Virtual Device on a VSX Gateway or VSX Cluster Member that implements the functionality of a Security Gateway. Acronym: VS.
Zero Touch
A simple Plug & Play setup process for installing an appliance - eliminating the need for technical expertise and having to connect to the appliance for initial configuration.
Gaia REST API
Gaia![]() Check Point security operating system that combines the strengths of both SecurePlatform and IPSO operating systems. REST API provides a new way to read and send information to servers that run Gaia Operating System. See sk143612.
Check Point security operating system that combines the strengths of both SecurePlatform and IPSO operating systems. REST API provides a new way to read and send information to servers that run Gaia Operating System. See sk143612.
CloudGuard IaaS
AWS Data Center enhancements:
-
Load Balancer (ALB and NLB) objects are supported.
-
Security Groups support the use of tags.
-
Subnet objects include IP addresses from all associated Network Interfaces.
Azure Data Center improvements:
-
Load Balancer (Public and Internal) objects are supported.
-
Load Balancers, Virtual Networks, and Network Security Groups support the use of tags.
-
Subnet objects include Front end IP addresses of the Internal Load Balancers.
Advanced Routing
-
Enhancements to OSPF and BGP allow to reset and restart OSPF neighbor adjacency per OSPF instance and BGP peering per peer.
-
Enhancing route refresh for improved handling of BGP routing inconsistencies.
New kernel capabilities
-
Upgraded Linux kernel
-
New partitioning system (
gpt):-
Supports more than 2TB physical/logical drives
-
-
Faster file system (xfs)
-
Supporting larger system storage (up to 48TB tested)
-
I/O related performance improvements
-
Multi-Queue - Full Gaia Clish
 The name of the default command line shell in Check Point Gaia operating system. This is a restricted shell (role-based administration controls the number of commands available in the shell). support for Multi-Queue commands
The name of the default command line shell in Check Point Gaia operating system. This is a restricted shell (role-based administration controls the number of commands available in the shell). support for Multi-Queue commands -
Added NFSv4 (client) support (NFS v4.2 is the default NFS version used)
-
Support of new system tools for debugging, monitoring and configuring the system
Security Management
Quantum Spark
1500 appliance series can be managed with R80.40 Security Management Server![]() Dedicated Check Point server that runs Check Point software to manage the objects and policies in a Check Point environment within a single management Domain. Synonym: Single-Domain Security Management Server. and R80.40 SmartProvisioning
Dedicated Check Point server that runs Check Point software to manage the objects and policies in a Check Point environment within a single management Domain. Synonym: Single-Domain Security Management Server. and R80.40 SmartProvisioning![]() Check Point Software Blade on a Management Server (the actual name is "Provisioning") that manages large-scale deployments of Check Point Security Gateways using configuration profiles. Synonyms: Large-Scale Management, SmartLSM, LSM..
Check Point Software Blade on a Management Server (the actual name is "Provisioning") that manages large-scale deployments of Check Point Security Gateways using configuration profiles. Synonyms: Large-Scale Management, SmartLSM, LSM..
Upgrade
A new report![]() Summary of network activity and Security Policy enforcement that is generated by Check Point products, such as SmartEvent. for Management Servers upgrades is available. The report shows the current status and progress and is located on the target machine under $MDS_FWDIR/log/upgrade_report-<timestamp>.html. For CPUSE upgrades, the report is available in the Upgrades (CPUSE) section of Gaia Portal.
Summary of network activity and Security Policy enforcement that is generated by Check Point products, such as SmartEvent. for Management Servers upgrades is available. The report shows the current status and progress and is located on the target machine under $MDS_FWDIR/log/upgrade_report-<timestamp>.html. For CPUSE upgrades, the report is available in the Upgrades (CPUSE) section of Gaia Portal.
Revert to Revision
The Security Management Server![]() Check Point Single-Domain Security Management Server or a Multi-Domain Security Management Server. architecture supports built-in revisions. Each publish operation saves a new revision that contains only the delta from the previous revision, allowing safe recovery from a crisis by restoring a Domain or a Management Server to a good known revision.
Check Point Single-Domain Security Management Server or a Multi-Domain Security Management Server. architecture supports built-in revisions. Each publish operation saves a new revision that contains only the delta from the previous revision, allowing safe recovery from a crisis by restoring a Domain or a Management Server to a good known revision.
Multi-Domain Server
-
Backup
 (1) In VRRP Cluster on Gaia OS - State of a Cluster Member that is ready to be promoted to Master state (if Master member fails). (2) In VSX Cluster configured in Virtual System Load Sharing mode with three or more Cluster Members - State of a Virtual System on a third (and so on) VSX Cluster Member. (3) A Cluster Member or Virtual System in this state does not process any traffic passing through cluster. and restore an individual Domain Management Server
(1) In VRRP Cluster on Gaia OS - State of a Cluster Member that is ready to be promoted to Master state (if Master member fails). (2) In VSX Cluster configured in Virtual System Load Sharing mode with three or more Cluster Members - State of a Virtual System on a third (and so on) VSX Cluster Member. (3) A Cluster Member or Virtual System in this state does not process any traffic passing through cluster. and restore an individual Domain Management Server Virtual Security Management Server that manages Security Gateways for one Domain, as part of a Multi-Domain Security Management environment. Acronym: DMS. on a Multi-Domain Server
Virtual Security Management Server that manages Security Gateways for one Domain, as part of a Multi-Domain Security Management environment. Acronym: DMS. on a Multi-Domain Server Dedicated Check Point server that runs Check Point software to host virtual Security Management Servers called Domain Management Servers. Synonym: Multi-Domain Security Management Server. Acronym: MDS..
Dedicated Check Point server that runs Check Point software to host virtual Security Management Servers called Domain Management Servers. Synonym: Multi-Domain Security Management Server. Acronym: MDS.. -
Migrate a Multi-Domain Security Management from one Multi-Domain Server to a different Multi-Domain Server.
-
Migrate a Security Management Server to become a Domain Management Server on a Multi-Domain Server.
-
Migrate a Domain Management Server to become a Security Management Server.
SmartTasks and API
-
DevOps teams can automate their security and transform it into DevSecOps workflows using Ansible and Terraform.
Automate security responses to threats, provision both physical and virtualized next-generation firewalls and automate routine configuration tasks, saving time and reducing configuration errors.
-
For more information about Check Point Ansible module, see Check Point Ansible security modules.
-
For more information about Check Point Terraform provider, see Check Point Terraform Provider.
-
-
New Management API authentication method that uses an auto-generated API Key.
-
New Management API commands to create cluster objects.
-
SmartTasks - Configure automatic scripts or HTTPS requests triggered by administrator tasks, such as publishing a session or installing a policy.
-
Significant increase of performance for multiple set/edit/delete object commands with Batch API.
CloudGuard Controller
-
Generate Events and Automatic Reactions based on CloudGuard Controller
 Provisions SDDC services as Virtual Data Centers that provide virtualized computer networking, storage, and security. logs and events.
Provisions SDDC services as Virtual Data Centers that provide virtualized computer networking, storage, and security. logs and events. -
Performance enhancements for connections to external Data Centers.
-
Integration with VMware NSX-T.
-
Support for additional API commands to create and edit Data Center
 Virtual centralized repository, or a group of physical networked hosts, Virtual Machines, and datastores. They are collected in a group for secured remote storage, management, and distribution of data. Server objects.
Virtual centralized repository, or a group of physical networked hosts, Virtual Machines, and datastores. They are collected in a group for secured remote storage, management, and distribution of data. Server objects.
SmartConsole
-
Central Deployment of Jumbo Hotfix Accumulators and Hotfixes from SmartConsole or with API supports multiple Security Gateways and Cluster installations in parallel.
-
Object search - support for partial word search using a wildcard. For example: when you search for
*oba, SmartConsole shows an existing object namedMyGlobalHost.
SmartEvent
Share SmartView views and reports with other administrators.
Log Exporter
-
Export logs filtered according to field values.
-
Generate SIEM compatible Threat Emulation and Forensics reports.
Endpoint Security
-
Collect Logs push operations - upload logs and debug information automatically to an FTP server.
-
Support for BitLocker encryption with Full Disk Encryption.
-
Support for external Certificate Authority certificates for Endpoint Security client authentication and communication with the Endpoint Security Management Server.
-
Support for dynamic size of Endpoint Security Client packages based on the selected features for deployment.
-
Policy can now control the level of notifications to end users.
-
Randomize the Malware scan time to make sure that not all computers do a scan at the same time. This makes sure that network performance is not affected by many simultaneous scans.
-
Uninstall Endpoint Security clients using a Challenge-Response process
-
Gaia Backup includes Endpoint Management components.
-
All client-server communication use HTTPS.
-
Endpoint Security Clients can connect to the Endpoint Security Management Server using FQDN in addition to the IP Address.
Licensing
For all license issues, contact Check Point Account Services.
