Basic QoS Architecture
The architecture and flow control of QoS![]() Check Point Software Blade on a Security Gateway that provides policy-based traffic bandwidth management to prioritize business-critical traffic and guarantee bandwidth and control latency. is similar to firewall.
Check Point Software Blade on a Security Gateway that provides policy-based traffic bandwidth management to prioritize business-critical traffic and guarantee bandwidth and control latency. is similar to firewall.
QoS has three components:
-
Gateway
The components can be installed on one machine or in a distributed configuration on a number of machines.
Bandwidth policy is configured using SmartConsole. On the Security Management Server![]() Check Point Single-Domain Security Management Server or a Multi-Domain Security Management Server., the policy is verified and installed on the QoS gateways. The QoS Security Gateway
Check Point Single-Domain Security Management Server or a Multi-Domain Security Management Server., the policy is verified and installed on the QoS gateways. The QoS Security Gateway![]() Dedicated Check Point server that runs Check Point software to inspect traffic and enforce Security Policies for connected network resources. uses:
Dedicated Check Point server that runs Check Point software to inspect traffic and enforce Security Policies for connected network resources. uses:
-
The firewall chaining mechanism to receive, process and send packets.
-
A proprietary classifying and rule
 Set of traffic parameters and other conditions in a Rule Base (Security Policy) that cause specified actions to be taken for a communication session.-matching infrastructure to examine a packet.
Set of traffic parameters and other conditions in a Rule Base (Security Policy) that cause specified actions to be taken for a communication session.-matching infrastructure to examine a packet.
Logging information is created using the firewall kernel API.
QoS Kernel Driver
The kernel driver is the heart of QoS operations. It is in the kernel driver that IP packets are examined, queued, scheduled and released, enabling QoS traffic control abilities.
QoS Daemon (fgd50)
The QoS daemon is a user mode process that:
-
Resolves DNS for the kernel (used for Rule Base
 All rules configured in a given Security Policy. Synonym: Rulebase. matching).
All rules configured in a given Security Policy. Synonym: Rulebase. matching). -
In a Cluster
 Two or more Security Gateways that work together in a redundant configuration - High Availability, or Load Sharing. Load Sharing configuration, updates the kernel of changes in the cluster status. For example, if a cluster member
Two or more Security Gateways that work together in a redundant configuration - High Availability, or Load Sharing. Load Sharing configuration, updates the kernel of changes in the cluster status. For example, if a cluster member Security Gateway that is part of a cluster. goes down. The daemon recalculates the relative loads of the gateways and updates the kernel.
Security Gateway that is part of a cluster. goes down. The daemon recalculates the relative loads of the gateways and updates the kernel.
QoS SmartConsole
You use SmartConsole and SmartDashboard![]() Legacy Check Point GUI client used to create and manage the security settings in versions R77.30 and lower. In versions R80.X and higher is still used to configure specific legacy settings. to create "bandwidth rules" for the QoS policy. Use the Logs & Monitor features in SmartConsole to see information about the active QoS Security Gateways and their Policies.
Legacy Check Point GUI client used to create and manage the security settings in versions R77.30 and lower. In versions R80.X and higher is still used to configure specific legacy settings. to create "bandwidth rules" for the QoS policy. Use the Logs & Monitor features in SmartConsole to see information about the active QoS Security Gateways and their Policies.
QoS SmartDashboard
Use SmartConsole to create and change QoS Policies. Use SmartDashboard to work with rules, together with their related network objects and services.
The QoS Policy rules are shown the QoS Rule Base.
QoS Configuration
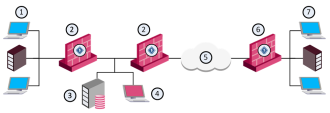
The Security Management Server and the QoS Security Gateway can be installed on the same machine or on two different machines. When they are installed on different machines, the configuration is known as distributed.
|
Item |
Description |
|---|---|
|
1 |
Internal network (main office) |
|
2 |
Security Gateway with QoS enabled |
|
3 |
Security Management Server |
|
4 |
SmartConsole |
|
5 |
Internet |
|
6 |
Security Gateway with QoS enabled (branch office) |
|
7 |
Internal network (branch office) |
The example shows a distributed configuration, in which one Security Management Server (consisting of a Security Management Server and a SmartConsole controls four QoS gateways. The four QoS gateways manage bandwidth allocation on three QoS enabled lines.
One Security Management Server can control and monitor multiple QoS gateways. The QoS Security Gateway operates independently of the Security Management Server. QoS gateways can operate on more Internet gateways and interdepartmental gateways.
Client-Server Interaction
SmartConsole and the Security Management Server can be installed on the same machine or on two different machines. When they are installed on two different machines, QoS implements the Client/Server model, in which a SmartConsole controls a Security Management Server.
|
Item |
Description |
|---|---|
|
1 |
Internal network (main office) |
|
2 |
Security Management Server |
|
3 |
SmartConsole |
|
4 |
Security Gateway with QoS enabled |
|
5 |
Internet |
In the configuration depicted in the above figure, the functionality of the Security Management Server is divided between two workstations (Tower and Bridge). The Security Management Server with the database is on Tower. The SmartConsole is on Bridge.
The user, working on Bridge, maintains the QoS Policy and database, which reside on Tower. The QoS Security Gateway on London enforces the QoS Policy on the QoS enabled line.
The Security Management Server is started with the cpstart command, and must be running if you wish to use the SmartConsole on one of the client machines.
A SmartConsole can manage the Server only if both the administrator logged into SmartConsole and the computer on which the SmartConsole is running have been authorized to access the Security Management Server. Use cpconfig to:
-
Add SmartConsole as GUI client authorized to access the Security Management Server
-
Define administrators for the Security Management Server.
Concurrent Sessions
More than one administrator can work with QoS Policies at the same time, each in a different session. A locking mechanism prevents administrators from working on the same object at one time. After you complete you work in a session, click Publish to make your changes available to other sessions and administrators.
Interaction with VPN
Interoperability
QoS and firewall share many core technology components. The same user-defined network objects can be used in both solutions. The integration of an organization's security and bandwidth management policies gives easy policy definition and system configuration. For efficient traffic inspection and enhanced performance, the blades share state table information. The QoS blade and firewall blade let users define bandwidth allocation rules for encrypted and NATed traffic.
Security Management Server
QoS uses the Security Management Server and shares the objects database (network objects, services and resources) with the firewall. Some objects have properties that are product specific. For example, the Firewall has encryption properties which are not related to QoS. A QoS network interface has speed properties that are not related to the firewall.