Bond Interfaces (Link Aggregation)
Check Point security devices support Link Aggregation, a technology that joins multiple physical interfaces into one virtual interface, known as a bond interface.
The bond interface share the load among many interfaces, which gives fault tolerance and increases throughput. Check Point devices support the IEEE 802.3ad Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP) for dynamic link aggregation.
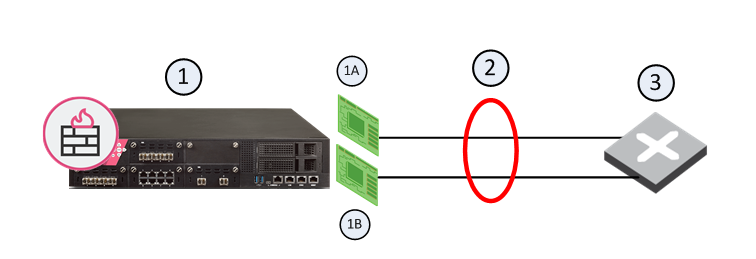
|
Item |
Description |
|---|---|
|
1 |
|
|
1A |
Interface 1 |
|
1B |
Interface 2 |
|
2 |
Bond Interface |
|
3 |
Router |
A bond interface (also known as a bonding group or bond) is identified by its Bond ID (for example: bond1) and is assigned an IP address. The physical interfaces included in the bond are called subordinate interfaces and do not have IP addresses.
You can configure a bond interface to use one of these functional strategies:
-
High Availability (Active/Backup): Gives redundancy when there is an interface or a link failure
 A hardware or software problem that causes a Security Gateway to be unable to serve as a Cluster Member (for example, one of cluster interface has failed, or one of the monitored daemon has crashed). Cluster Member that suffered from a failure is declared as failed, and its state is changed to Down (a physical interface is considered Down only if all configured VLANs on that physical interface are Down).. This strategy also supports switch redundancy. Bond High Availability
A hardware or software problem that causes a Security Gateway to be unable to serve as a Cluster Member (for example, one of cluster interface has failed, or one of the monitored daemon has crashed). Cluster Member that suffered from a failure is declared as failed, and its state is changed to Down (a physical interface is considered Down only if all configured VLANs on that physical interface are Down).. This strategy also supports switch redundancy. Bond High Availability A redundant cluster mode, where only one Cluster Member (Active member) processes all the traffic, while other Cluster Members (Standby members) are ready to be promoted to Active state if the current Active member fails. In the High Availability mode, the Cluster Virtual IP address (that represents the cluster on that network) is associated: (1) With physical MAC Address of Active member (2) With virtual MAC Address. Synonym: Active/Standby. Acronym: HA. works in Active/Backup mode - interface Active
A redundant cluster mode, where only one Cluster Member (Active member) processes all the traffic, while other Cluster Members (Standby members) are ready to be promoted to Active state if the current Active member fails. In the High Availability mode, the Cluster Virtual IP address (that represents the cluster on that network) is associated: (1) With physical MAC Address of Active member (2) With virtual MAC Address. Synonym: Active/Standby. Acronym: HA. works in Active/Backup mode - interface Active State of a Cluster Member that is fully operational: (1) In ClusterXL, this applies to the state of the Security Gateway component (2) In 3rd-party / OPSEC cluster, this applies to the state of the cluster State Synchronization mechanism./Standby
State of a Cluster Member that is fully operational: (1) In ClusterXL, this applies to the state of the Security Gateway component (2) In 3rd-party / OPSEC cluster, this applies to the state of the cluster State Synchronization mechanism./Standby State of a Cluster Member that is ready to be promoted to Active state (if the current Active Cluster Member fails). Applies only to ClusterXL High Availability Mode. mode. When an Active subordinate interface is down
State of a Cluster Member that is ready to be promoted to Active state (if the current Active Cluster Member fails). Applies only to ClusterXL High Availability Mode. mode. When an Active subordinate interface is down State of a Cluster Member during a failure when one of the Critical Devices reports its state as "problem": In ClusterXL, applies to the state of the Security Gateway component; in 3rd-party / OPSEC cluster, applies to the state of the State Synchronization mechanism. A Cluster Member in this state does not process any traffic passing through cluster., the connection automatically fails over to the primary subordinate interface. If the primary subordinate interface is not available, the connection fails over to a different subordinate interface.
State of a Cluster Member during a failure when one of the Critical Devices reports its state as "problem": In ClusterXL, applies to the state of the Security Gateway component; in 3rd-party / OPSEC cluster, applies to the state of the State Synchronization mechanism. A Cluster Member in this state does not process any traffic passing through cluster., the connection automatically fails over to the primary subordinate interface. If the primary subordinate interface is not available, the connection fails over to a different subordinate interface. -
Load Sharing (Active/Active): All subordinate interfaces in the UP state are used simultaneously. Traffic is distributed among the subordinate interfaces to maximize throughput. Bond Load Sharing
 A redundant cluster mode, where all Cluster Members process all incoming traffic in parallel. For more information, see "Load Sharing Multicast Mode" and "Load Sharing Unicast Mode". Synonyms: Active/Active, Load Balancing mode. Acronym: LS. does not support switch redundancy.
A redundant cluster mode, where all Cluster Members process all incoming traffic in parallel. For more information, see "Load Sharing Multicast Mode" and "Load Sharing Unicast Mode". Synonyms: Active/Active, Load Balancing mode. Acronym: LS. does not support switch redundancy.
Note - Bonding Load Sharing mode requires SecureXL
 Check Point product on a Security Gateway that accelerates IPv4 and IPv6 traffic that passes through a Security Gateway. to be enabled on Security Gateway or each Cluster Member
Check Point product on a Security Gateway that accelerates IPv4 and IPv6 traffic that passes through a Security Gateway. to be enabled on Security Gateway or each Cluster Member Security Gateway that is part of a cluster..
Security Gateway that is part of a cluster..You can configure Bond Load Sharing to use one of these modes:
-
Round Robin - Selects the Active subordinate interfaces sequentially.
-
802.3ad (LACP) - Dynamically uses Active subordinate interfaces to share the traffic load. This mode uses the LACP protocol, which fully monitors the interface link between the Check Point Security Gateway and a switch.
-
XOR - All subordinate interfaces in the UP state are Active for Load Sharing. Traffic is assigned to Active subordinate interfaces based on the transmit hash policy: Layer 2 information (XOR of hardware MAC addresses), or Layer 3+4 information (IP addresses and Ports).
-
For Bonding High Availability mode and for Bonding Load Sharing mode:
-
The number of bond interfaces that can be defined is limited by the maximal number of interfaces supported by each platform. See the R80.40 Release Notes.
-
Up to 8 physical subordinate interfaces can be configured in a single bond interface.
