

By default, all BGP peers in an Autonomous System (AS) are in a full mesh. However, if an AS has many BGP peers, the BGP configuration and hardware deployment is not easy.
To simplify configuration and deployment and avoid having to connect the peers in a full mesh, it is possible to configure:
The route reflector and its clients are known as a route reflection cluster. The route reflector sends the routes received from its peers to its clients.
In the example network, AS1 has five BGP-enabled Check Point routers. One of the routers is a route reflector for two clients.
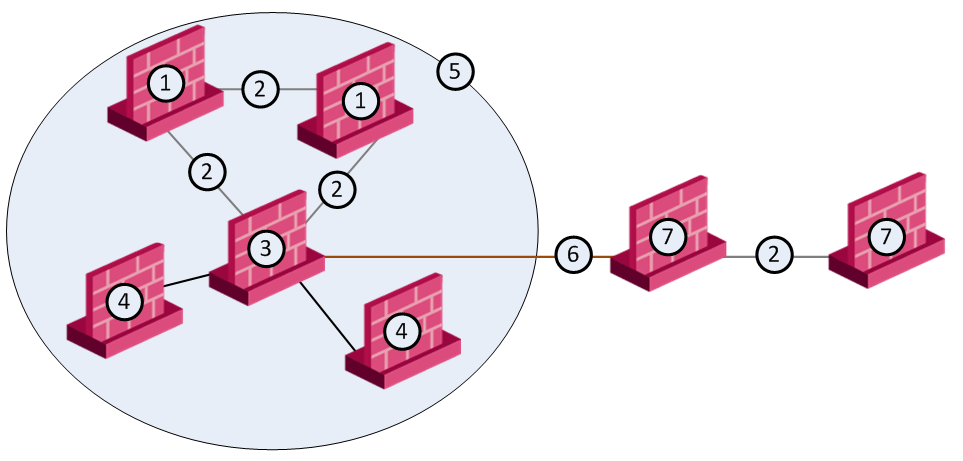
Number |
Description |
|
Number |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 |
Non-clients |
|
5 |
AS1 |
2 |
IBGP |
|
6 |
EBGP |
3 |
Route Reflector in cluster |
|
7 |
AS676 |
4 |
Clients in cluster |
|
|
|
It is possible to define more than one route reflector in the AS to avoid having a single point of failure.
Best Practice - We recommend that you not use multiple redundant reflectors unnecessarily because it increases the memory required to keep routes on the peers of redundant reflectors.
To learn more about route reflection, see RFC 2796.