

You can install ClusterXL on Check Point appliances in one of these configurations:
You can install ClusterXL on Open Servers only in a distributed configuration - the Cluster Members and the Security Management Server are installed on different computers.
To see the ClusterXL supported platforms, see the R80.30 Release Notes.
For installation instructions, see the R80.30 Installation and Upgrade Guide.
Note - Configuring more than 4 members significantly decreases cluster performance due to amount of Delta Sync.
ClusterXL operation completely relies on internal timers and calculation of internal timeouts, which are based on hardware clock ticks.
Therefore, in order to avoid unexpected behavior, ClusterXL is supported only between machines with identical CPU characteristics.
In addition, in order to avoid unexpected fail-overs due to issues with CCP packets on cluster interfaces, we strongly recommend to pair only identical physical interfaces as cluster interfaces - even when connecting the Cluster Members via a switch. For example:
Note - There is no requirement for throughput of Sync interface to be identical to, or larger than throughput of traffic interfaces (although, to prevent a possible bottle neck, a good practice for throughput of Sync interface is to be at least identical to throughput of traffic interfaces).
Important:
|
ClusterXL is supported only between identical operating systems - all Cluster Members must be installed on the same operating system).
ClusterXL is supported only between identical Check Point software versions - all Cluster Members must be installed with identical Check Point software, including OS build and hotfixes.
All Check Point software components must be the same on all Cluster Members. Meaning that the same Software Blades and features must be enabled on all Cluster Members:
Notes:
Otherwise, traffic might not be processed as expected and/or state of Cluster Members might change expectedly. In addition, Full Sync will fail.
The Cluster is usually located in an environment having other networking devices, such as switches and routers. These devices and the Cluster Members must interact to assure network connectivity. This section outlines the requirements imposed by ClusterXL on surrounding networking equipment.
When using CCP in multicast mode, configure these settings on the switch:
By default, when ClusterXL is configured in High Availability mode or Load Sharing Unicast Mode, Cluster Members send the Cluster Control Protocol (CCP) packets in Multicast mode (the Layer 2 destination MAC address in the CCP packets is a multicast MAC address 01:00:5e:X:X:X). To let the CCP packets pass between Cluster Members, configure the settings below on the surrounding switches.
Switch Setting |
Explanation |
|---|---|
IGMP and Static CAMs |
IGMP registration (also known as IGMP Snooping) is enabled by default on Cluster Members. You can disable IGMP registration on Cluster Members. In scenarios, where disabling IGMP registration is problematic, you can configure Static CAMs on switches to allow multicast traffic on specified switch ports. |
Disabling multicast limits |
Certain switches have an upper limit on the number of broadcasts and multicasts that they can pass, in order to prevent broadcast storms. This limit is usually a percentage of the total interface bandwidth. It is possible to either turn off broadcast storm control, or to allow a higher level of broadcasts or multicasts through the switch. If the connecting switch is incapable of having any of these settings configured, it is possible, though less efficient, for the switch to use broadcast to forward traffic, and to configure the Cluster Members to use broadcast CCP. |
When using CCP in multicast mode, configure these settings on the router:
By default, when ClusterXL is configured in High Availability mode or Load Sharing Unicast Mode, the unicast Cluster Virtual IP addresses are mapped to unicast MAC addresses of the physical interfaces on the Active or Pivot Cluster Member. To let the traffic reach the cluster, configure the settings below on the surrounding routers.
Router Setting |
Explanation |
|---|---|
Unicast MAC |
The router needs to be able to learn this MAC through regular ARP messages. |
When working with Load Sharing in Multicast mode, configure the following settings on the switch:
By default, when ClusterXL is configured in Load Sharing Multicast Mode, Cluster Members send the Cluster Control Protocol (CCP) packets in Multicast mode (the Layer 2 destination MAC address in the CCP packets is a multicast MAC address 01:00:5e:X:X:X).
Switch Setting |
Explanation |
|---|---|
Port Mirroring |
ClusterXL in Load Sharing Multicast mod does not support the use of unicast MAC addresses with Port Mirroring. |
When working with Load Sharing in Multicast mode, configure the following settings on the router:
By default, when ClusterXL is configured in High Availability mode or Load Sharing Multicast Mode, the unicast Cluster Virtual IP addresses are mapped to multicast MAC addresses (these are generated automatically by the Management Server based on the configured Cluster Virtual IP addresses). To let the traffic reach the cluster, the router must support sending unicast IP packets with multicast MAC addresses.
Router Setting |
Explanation |
|---|---|
Static MAC |
Most routers can add ARP entries with a unicast IP address and a multicast MAC address automatically. If you have a router that is not able to learn this type of mapping dynamically, you need to configure static MAC entries to map unicast Cluster Virtual IP addresses to multicast MAC addresses. |
IGMP and Static CAMs |
Some routers require disabling of IGMP snooping, or configuration of static CAMs to support sending of unicast IP packets with multicast MAC addresses. |
Disabling multicast limits |
Certain routers have an upper limit on the number of broadcasts and multicasts that they can pass, in order to prevent broadcast storms. This limit is usually a percentage of the total interface bandwidth. It is possible to either turn off broadcast storm control, or to allow a higher limit of broadcasts or multicasts through the router. |
Disabling forwarding of multicast traffic to the router itself |
Some routers send multicast traffic to the router itself. This may cause a multicast storm through the network. Disable such configuration on your router. |
When ClusterXL is configured in HA mode or Load Sharing Unicast mode (not Multicast) a single Cluster Member is associated with the Cluster Virtual IP address. In a High Availability environment, the single member is the Active member. In a Load Sharing environment, the single member is the Pivot.
After fail-over, the new Active member (or Pivot member) broadcasts a series of Gratuitous ARP Requests (G-ARPs). The G-ARPS associate the Virtual IP address of the cluster with the physical MAC address of the new Active member or the new Pivot. When this happens:
Switches may not integrate these GARP updates quickly enough into their ARP tables. Switches continue to send traffic to the physical MAC address of the member that failed. This results in traffic outage until the switches have fully updated ARP cache tables.
These components continue to send traffic to the MAC address of the failed member.
To minimize possible traffic outage during a fail-over, configure the cluster to use a virtual MAC address (VMAC).
By enabling Virtual MAC in ClusterXL High Availability mode, or Load Sharing Unicast mode, all Cluster Members associate the same Virtual MAC address with all Cluster Virtual Interfaces and the Virtual IP address. In Virtual MAC mode, the VMAC that is advertised by the Cluster Members (through G-ARP Requests) keeps the real MAC address of each member and adds a Virtual MAC address on top of it.
For local connections and sync connections, the real physical MAC address of each Cluster Member is still associated with its real IP address.
Note - Traffic originating from the Cluster Members will be sent with the VMAC Source address.
You can enable VMAC in SmartConsole, or on the command line. See sk50840.
Failover time in a cluster with enabled VMAC mode is shorter than a failover in a cluster that uses a physical MAC addresses.
To configure VMAC Mode using SmartConsole:
To configure VMAC Mode using the command line:
On each Cluster Member, set the same value for the global kernel parameter fwha_vmac_global_param_enabled.
fw ctl get int fwha_vmac_global_param_enabled
To enable VMAC mode: fw ctl set int fwha_vmac_global_param_enabled 1
To disable VMAC mode: fw ctl set int fwha_vmac_global_param_enabled 0
In Gaia Clish: show cluster members interfaces all
In the Expert mode: cphaprob -a if
When VMAC mode is enabled, output of this command shows the VMAC address of each virtual cluster interface.
Follow the instructions in sk26202 to add this line to the $FWDIR/boot/modules/fwkern.conf file:
fwha_vmac_global_param_enabled=<value>
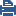
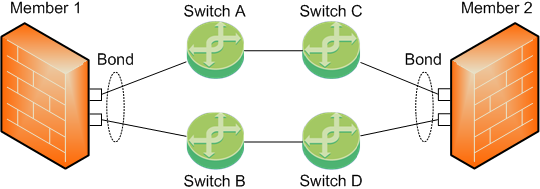
Topology 1
To work with this topology, you can configure the Bond interface in High Availability or Load Sharing mode.
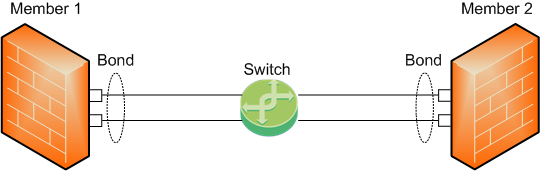
Topology 2
To work with this topology, you can configure the Bond interface in High Availability or Load Sharing mode.
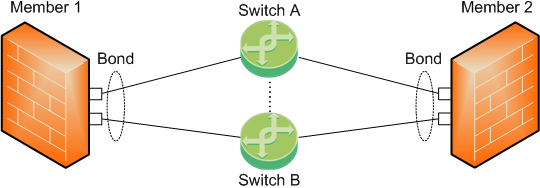
Topology 3 (new in R80.20: Enhanced Active/Backup Bond)
To work with this topology, you must configure the Bond interface in High Availability mode.
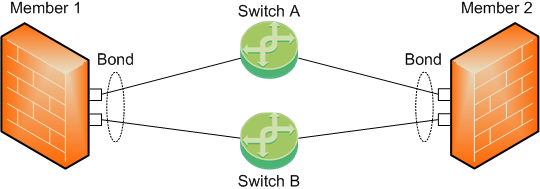
Topology 4 (new in R80.20: Enhanced Active/Backup Bond)
To work with this topology, you must configure the Bond interface in High Availability mode.
When using ClusterXL, make sure to synchronize the clocks of all of the Cluster Members. You can synchronize the clocks manually, or using a protocol such as NTP. Features, such as VPN, only function properly when the clocks of all of the Cluster Members are synchronized.
R80.30 ClusterXL supports High Availability clusters for IPv6. IPv6 status information is synchronized and the IPv6 clustering mechanism is activated during failover.
You can define IPv6 addresses for:
Limitations
During failover, a cluster sends gratuitous ARP request packets to update hosts and routers connected to cluster interfaces. It does this by advertising the new MAC address for the virtual cluster IPv4 addresses.
ClusterXL updates the IPv6 network during failovers. ClusterXL sends Neighbor Advertisement messages to update the neighbor cache (which is equivalent to the ARP cache in IPv4) by advertising the new MAC address for the virtual cluster IPv6 address. In addition, ClusterXL will reply to any Neighbor Solicitation with a target address equal to the Virtual Cluster IPv6 address.
Note - ClusterXL failover event detection is based on IPv4 probing. During state transition the IPv4 driver instructs the IPv6 driver to reestablish IPv6 network connectivity to the HA cluster.
The following restrictions apply when you synchronize Cluster Members:
Synchronization interface redundancy is not supported for VRRP Clusters. See sk92804.
The reason for these restrictions is that the user authentication state is maintained by a process on the Security Gateway. It cannot be synchronized on Cluster Members in the same way as kernel data is synchronized. However, the states of Session Authentication and Client Authentication are saved in kernel tables, and can be synchronized.