

This example shows:
Related documentation:
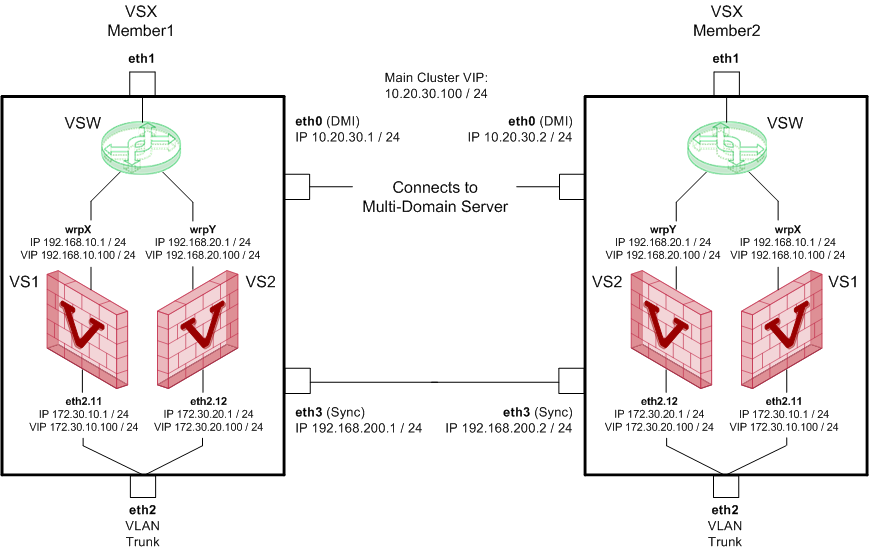
Topology of the VSX Cluster:
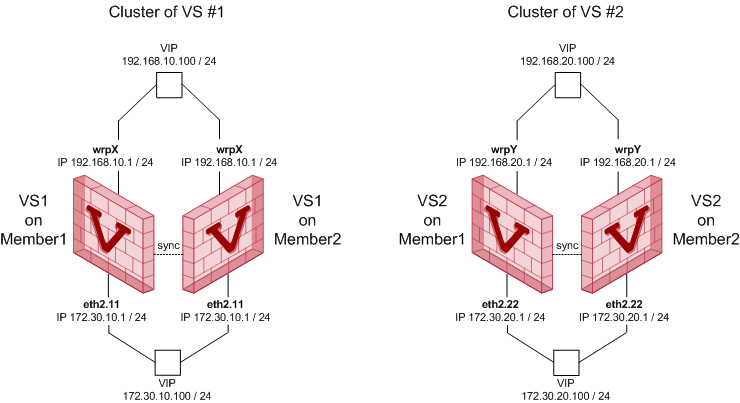
Topology of the Virtual Systems in the cluster:
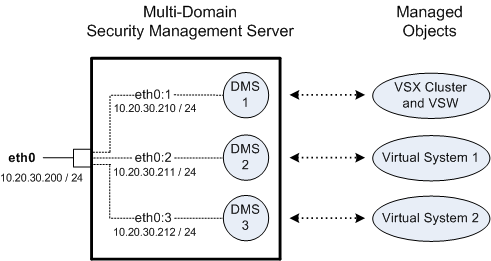
Multi-Domain Server and managed objects:
Interfaces and IP addresses:
Computer |
Interface |
IP Address / Net Mask |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
VSX |
eth0 |
10.20.30.1/24 Main Cluster VIP 10.20.30.100/24 |
Dedicated Management Interface (DMI) |
|
eth1 |
none |
External physical interface |
|
wrpX |
192.168.10.1/24 Cluster VIP 192.168.10.100/24 |
External warp interface on Virtual System 1 Note - Interface name is generated automatically |
|
wrpY |
192.168.20.1/24 VIP 192.168.20.100/24 |
External warp interface on Virtual System 2 Note - Interface name is generated automatically |
|
eth2 |
none |
Internal physical interface - VLAN Trunk |
|
eth2.11 |
172.30.10.1/24 Cluster VIP 172.30.10.100/24 |
Internal VLAN interface on Virtual System 1 |
|
eth2.22 |
172.30.20.1/24 Cluster VIP 172.30.10.100/24 |
Internal VLAN interface on Virtual System 2 |
|
eth3 |
192.168.200.1/24 |
Cluster Sync physical interface |
VSX |
eth0 |
10.20.30.2/24 Cluster VIP 10.20.30.100/24 |
Dedicated Management Interface (DMI) |
|
eth1 |
none |
External physical interface |
|
wrpX |
192.168.10.2/24 Cluster VIP 192.168.10.100/24 |
External warp interface on Virtual System 1 Note - Interface name is generated automatically |
|
wrpY |
192.168.20.2/24 Cluster VIP 192.168.20.100/24 |
External warp interface on Virtual System 2 Note - Interface name is generated automatically |
|
eth2 |
none |
Internal physical interface - VLAN Trunk |
|
eth2.11 |
172.30.10.2/24 Cluster VIP 172.30.10.100/24 |
Internal VLAN interface on Virtual System 1 |
|
eth2.22 |
172.30.10.2/24 Cluster VIP 172.30.10.100/24 |
Internal VLAN interface on Virtual System 2 |
|
eth3 |
192.168.200.2/24 |
Cluster Sync physical interface |
Multi- |
eth0 |
10.20.30.200/24 |
Leading Interface that belongs to the Multi-Domain Server |
|
eth0:1 |
10.20.30.210/24 |
Virtual interface that belongs to the Main Domain Management Server (DMS 1), which manages the VSX Cluster and Virtual Switch |
|
eth0:2 |
10.20.30.211/24 |
Virtual interface that belongs to the Target Domain Management Server (DMS 2), which manages the Virtual System 1 |
|
eth0:3 |
10.20.30.212/24 |
Virtual interface that belongs to the Target Domain Management Server (DMS 3), which manages the Virtual System 2 |
Step |
Description |
|---|---|
1 |
Install a Check Point appliance or Open Server. |
2 |
Install Gaia OS. |
3 |
Run the Gaia First Time Configuration Wizard. These settings are specific to the Multi-Domain Server:
|
4 |
Install the applicable licenses. |
5 |
Configure the applicable settings:
|
Step |
Description |
|---|---|
1 |
Connect with SmartConsole to the Multi-Domain Server. |
2 |
Create a new Domain and Domain Server. In our example:
|
3 |
Publish the session. |
4 |
Configure the Main Domain Management Server:
|
Step |
Description |
|---|---|
1 |
Connect with SmartConsole to the Multi-Domain Server. |
2 |
Create a new Domain and Domain Server. In our example:
|
3 |
Publish the session. |
4 |
Configure the Target Domain Management Server:
|
Step |
Description |
|---|---|
1 |
Connect with SmartConsole to the Multi-Domain Server. |
2 |
Create a new Domain and Domain Server. In our example:
|
3 |
Publish the session. |
4 |
Configure the Target Domain Management Server:
|
Step |
Description |
|---|---|
1 |
Install a Check Point appliance or Open Server. |
2 |
Make sure you have enough physical interfaces for your VSX topology. |
3 |
Install Gaia OS. |
4 |
Run the Gaia First Time Configuration Wizard. These settings are specific to the VSX Cluster Member 1:
|
5 |
Make sure to enable the applicable physical interfaces: To enable a physical interface in Gaia Portal
To enable a physical interface in Gaia Clish, run:
|
6 |
Install the applicable licenses. |
Step |
Description |
|---|---|
1 |
Install a Check Point appliance or Open Server. |
2 |
Make sure you have enough physical interfaces for your VSX topology. |
3 |
Install Gaia OS. |
4 |
Run the Gaia First Time Configuration Wizard. These settings are specific to the VSX Cluster Member 1:
|
5 |
Make sure to enable the applicable physical interfaces: To enable a physical interface in Gaia Portal
To enable a physical interface in Gaia Clish, run:
|
6 |
Install the applicable licenses. |
See Introduction to VSX Clusters and Creating VSX Clusters.
Step |
Description |
|---|---|
1 |
Connect with SmartConsole to the Main Domain Management Server that manages the objects of the VSX Cluster and Virtual Switch. In our example: |
2 |
At the top, click Objects > More object types > Network Object > Gateways and Servers > VSX > New Cluster. |
3 |
On the VSX Cluster General Properties (Specify the object's basic settings) page:
|
4 |
On the Virtual Systems Creation Templates (Select the Creation Template most suitable for your VSX deployment) page:
|
5 |
On the VSX Cluster Members (Define the members of this VSX Cluster) page: Add the first VSX Cluster Member:
|
|
If the Trust State field does not show Trust established, perform these steps:
|
6 |
On the VSX Cluster Members (Define the members of this VSX Cluster) page: Add the second VSX Cluster Member:
|
|
If the Trust State field does not show Trust established, perform these steps:
|
7 |
On the VSX Cluster Interfaces (Physical Interfaces Usage) page:
|
8 |
On the VSX Cluster members (Synchronization Network) page:
|
9 |
On the Virtual Network Device Configuration (Specify the object's basic settings) page:
|
10 |
On the VSX Gateway Management (Specify the management access rules) page:
Important - These access rules apply only to the VSX Gateway (context of VS0), which is not intended to pass any "production" traffic. |
11 |
On the VSX Gateway Creation Finalization page:
|
12 |
Examine the VSX configuration:
|
See Working with VSX Clusters.
Step |
Description |
|---|---|
1 |
From the left navigation toolbar, click Gateways & Servers. |
2 |
Open the VSX Cluster object. In our example: |
3 |
Enable the applicable Software Blades. Refer to:
|
4 |
Configure other applicable settings. |
5 |
Click OK to push the updated VSX Configuration. Click View Report for more information. |
6 |
Install policy on the VSX Cluster object:
|
7 |
Examine the VSX configuration:
|
Step |
Description |
|---|---|
1 |
Connect with SmartConsole to the Main Domain Management Server that manages the objects of the VSX Cluster and Virtual Switch. In our example: |
2 |
Create the Virtual Switch object: At the top, click Objects > More object types > Network Object > Gateways and Servers > VSX > New Virtual Switch. |
3 |
On the VSX Switch General Properties (Define the object name and the hosting VSX) page:
|
4 |
On the VSX Switch Network Configuration (Define Virtual Switch Interfaces) page:
|
5 |
On the VSX Switch Cluster Creation Finalization page:
|
6 |
Examine the VSX configuration:
|
Step |
Description |
1 |
Connect with SmartConsole to the Target Domain Management Server that manages the object of the first Virtual System. In our example: |
2 |
In SmartConsole, create the first Virtual System object: See Creating a New Virtual System. At the top, click Objects > More object types > Network Object > Gateways and Servers > VSX > New Virtual System. |
3 |
On the VSX System General Properties (Define the object name and the hosting VSX) page:
|
4 |
On the Virtual System Network Configuration (Define Virtual System Interfaces and Routes) page: In our example, this Virtual System connects to the Virtual Switch ("external") and to the physical VLAN Trunk interface ("internal") on the VSX Cluster Members. In the Interfaces section, add the "external" interface:
|
|
In the Interfaces section, add the "internal" interface:
In the Routes section, click Add to configure the applicable static routes and the Default Route. Click Next. |
5 |
On the Virtual System Cluster Creation Finalization page:
|
6 |
Examine the VSX configuration:
|
See Modifying a Virtual System.
Step |
Description |
|---|---|
1 |
From the left navigation toolbar, click Gateways & Servers. |
2 |
Open the first Virtual System object. In our example: |
3 |
Enable the applicable Software Blades. In our example: I Refer to:
|
4 |
Configure other applicable settings. |
5 |
Click OK to push the updated VSX Configuration. |
6 |
Configure and install the applicable policy on the first Virtual System object. |
7 |
Examine the VSX configuration:
|
Step |
Description |
|---|---|
1 |
Connect with SmartConsole to the Target Domain Management Server that manages the object of the first Virtual System. In our example: |
2 |
In SmartConsole, create the first Virtual System object: See Creating a New Virtual System. At the top, click Objects > More object types > Network Object > Gateways and Servers > VSX > New Virtual System. |
3 |
On the VSX System General Properties (Define the object name and the hosting VSX) page:
|
4 |
On the Virtual System Network Configuration (Define Virtual System Interfaces and Routes) page: In our example, this Virtual System connects to the Virtual Switch ("external") and to the physical VLAN Trunk interface ("internal") on the VSX Cluster Members. In the Interfaces section, add the "external" interface:
|
|
In the Interfaces section, add the "internal" interface:
In the Routes section, click Add to configure the applicable static routes and the Default Route. Click Next. |
5 |
On the Virtual System Cluster Creation Finalization page:
|
6 |
Examine the VSX configuration:
|
See Modifying a Virtual System.
Step |
Description |
|---|---|
1 |
From the left navigation toolbar, click Gateways & Servers. |
2 |
Open the second Virtual System object. In our example: |
3 |
Enable the applicable Software Blades. In our example: M Refer to:
|
4 |
Configure other applicable settings. |
5 |
Click OK to push the updated VSX Configuration. |
6 |
Configure and install the applicable policy on the second Virtual System object. |
7 |
Examine the VSX configuration:
|