

An event is a record of a security incident. It is based on one or more logs, and on rules that are defined in the Event Policy.
An example of an event that is based on one log: A High Severity Anti-Bot event. One Anti-Bot log with a Severity of High causes the event to be recorded.
An example of an event that is based on more than one log: A Certificate Sharing event. Two login logs with the same certificate and a different user cause the event to be recorded.
SmartEvent automatically defines logs that are not Firewall, VPN, or HTTPS Inspection logs, as events.
Events that are based on a suspicious pattern of two or more logs, are created by the SmartEvent Correlation Unit. These correlated events are defined in the SmartEvent client GUI, in the Policy tab.
Most logs are Firewall, VPN and HTTPS inspection logs. Therefore, SmartEvent does not define them as events by default to avoid a performance impact on the SmartEvent Server. For logs from R77.xx Gateways and lower: To create events for Firewall, in the SmartEvent Policy tab, enable Consolidated Sessions > Firewall Session.
To show an Internet browsing event:
The events of this time period show.
This is an example log of a High Risk event.
uTorrent is classified as a High risk application. It is a freeware closed source BitTorrent client.
SmartEvent has some components that work together to help track down security threats and make your network more secure.
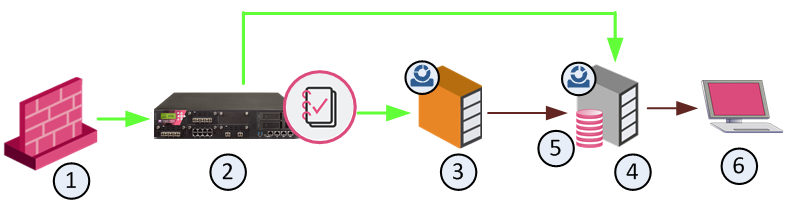
This is how they work together. The numbers refer to the diagram:
Item |
Description |
Purpose |
|---|---|---|
|
|
Log data flow |
|
|
Event data flow |
1 |
Check Point Security Gateway |
Sends logs to the Log Server. |
2 |
Log Server |
Stores logs. |
3 |
SmartEvent Correlation Unit |
Identifies events: Analyzes each log entry from a Log Server, and looks for patterns according to the installed Event Policy. The logs contain data from Check Point products and certain third-party devices. When a threat pattern is identified, the SmartEvent Correlation Unit forwards the event to the SmartEvent Server. |
4 |
SmartEvent Server |
Receives the items that are identified as events by the SmartEvent Correlation Unit. The SmartEvent Server does further analysis to determine the severity level of the event and what action to do. The event is stored in the system database. |
5 |
Events database |
Stores events. Located on the SmartEvent Server. |
6 |
SmartEvent client |
Shows the received events. Uses the clients to manage events (for example: to filter and close events), fine-tunes, and installs the Event Policy. The clients are:
|
The SmartEvent components can be installed on one computer (that is, a standalone deployment) or multiple computers and sites (a distributed deployment). To handle higher volumes of logging activity, we recommend a distributed deployment. You can install more than one SmartEvent Correlation Unit. Each SmartEvent Correlation Unit can analyze logs from more than one Log Server or Domain Log Server.