

Best practice - Configure anti-spoofing on the Check Point gateway interfaces.
It is not necessary to define a rule that specifies which port to open and which endpoint can talk. The gateway automatically gets this information from the signaling. For a given H.323 signaling rule (with RAS and/or H.323 services), the gateway automatically opens ports for the H.245 connections and RTP/RTCP media stream connections.
For example, if the Connect message identifies port 80 as the H.245 port, the port will not be opened.
The Check Point Security Gateway window shows.
Note - Rematch connections is selected by default.
Note – The old policy rules are still intact for calls already in-progress and they will not be dropped.
These predefined H.323 services are available:
Service |
Purpose |
|---|---|
TCP:H323 |
Allows a Q.931 to be opened (and if needed, dynamically opens an H.245 port), and dynamically opens ports for RTP/RTCP or T.120. |
UDP:H323_ras |
Allows a RAS port to be opened, and then dynamically opens a Q.931 port (an H.245 port if needed). Also dynamically opens and RTP/RTCP and T.120 ports. |
UDP:H323_ras_only |
Allows only RAS ports. Cannot be used to make calls. If this service is used, no Application Intelligence Checks (payload inspection or modification as NAT translation) are made. Do not use if you want to perform NAT on RAS messages. Do not use in the same rule as the |
TCP:H323_any |
Relevant only for versions prior to R75.40VS: Similar to the H323 service, but also allows the Destination in the rule to be ANY rather than a network object. Only use |
Note - Make sure to use the H.323 and H.323_ras services in H.323 Security Gateways rules.
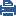
An endpoint-to-endpoint topology is shown in the image, with Net_A and Net_B on opposite sides of the gateway. This procedure explains:
No incoming calls can be made when Hide NAT is configured for the internal phones.
VoIP rule for this scenario:
Source |
Destination |
Services & Applications |
Action |
|---|---|---|---|
Net_A Net_B |
Net_B Net_A |
H323 |
Accept |
To define an H.323 rule for endpoint-to-endpoint topology:
If you select Hide NAT:
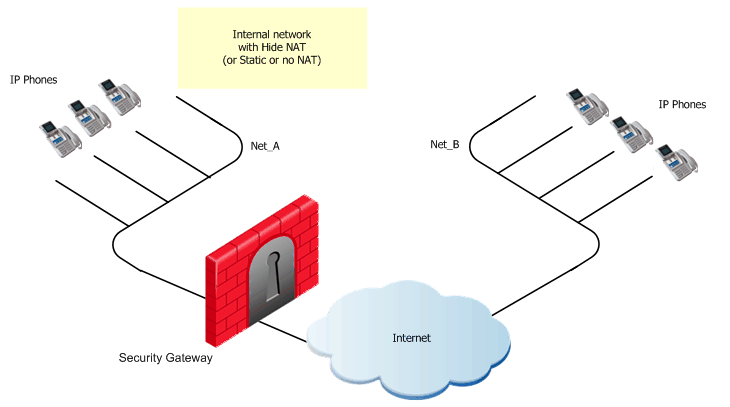
A Gatekeeper-to-Gatekeeper topology is shown in the image, with Net_A and Net_B on opposite sides of the gateway. This procedure shows you how to:
VoIP rule for this scenario:
Source |
Destination |
Service |
Action |
Comment |
|---|---|---|---|---|
GK_A GK_B |
GK_B GK_A |
H323 H323_ras |
Accept |
Bidirectional calls |
To define an H.323 rule for Gatekeeper-to-Gatekeeper topology:
In the image, these are Net_A and Net_B.
To define Hide NAT or Static NAT for the phones in the internal network, edit the network object for Net_A.
H323_ras service greater or equal to the Gatekeeper registration time-out. The Inspection Settings window opens.
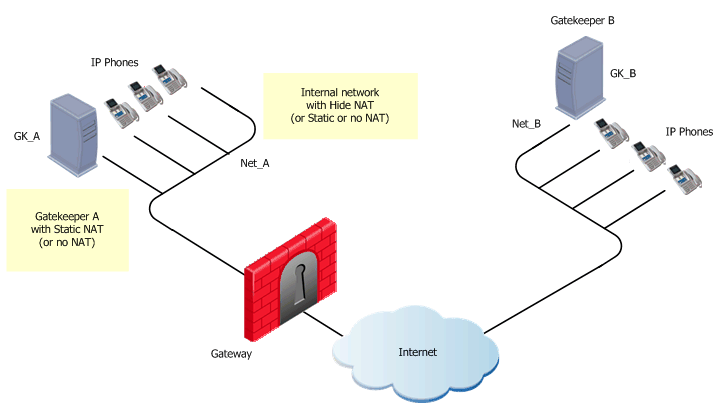
The illustration shows a Gateway-to-Gateway topology, with Net_A and Net_B on opposite sides of the gateway. This procedure shows you how to:
VoIP rule for this scenario:
Source |
Destination |
Service |
Action |
Comment |
|---|---|---|---|---|
GW_A GW_B |
GW_B GW_A |
H323 |
Accept |
Bidirectional calls |
To define an H.323 rule for gateway-to-gateway topology:
For this example, these are Net_A and Net_B.
To define Hide NAT or Static NAT for the phones in the internal network, edit the network object for Net_A.
To define Static NAT for the Gatekeeper/Gateway in the internal network, do step 4 again for the Gatekeeper/Gateway object (GK_A).
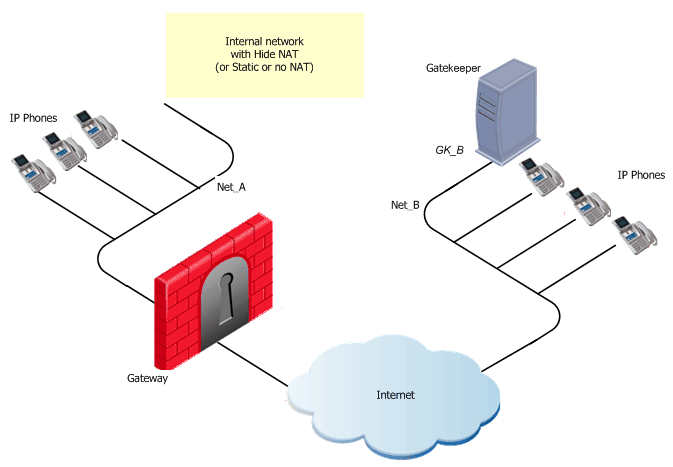
This figure shows an H.323 topology with a Gatekeeper in the Internet, with Net_A and Net_B on opposite sides of the gateway. This procedure explains how to:
VoIP rule for this scenario:
Source |
Destination |
Services & Applications |
Action |
Comment |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Net_A Net_B GK_B |
GK_B Net_A |
H323_ras |
Accept |
Bidirectional calls. |
To define an H.323 rule for a Gatekeeper in the external network:
In the image, these are Net_A and Net_B.
To define Hide NAT or Static NAT for the phones in the internal network, edit the network object for Net_A.
If you select Hide NAT:
H323_ras service greater or equal to the Gatekeeper registration time-out. The Inspection Settings window opens.
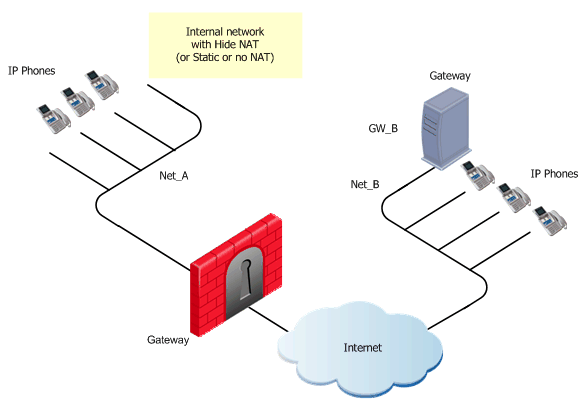
The image shows an H.323 topology with a Gateway in the Internet, with Net_A and Net_B on opposite sides of the gateway. This procedure shows you how to:
VoIP rule for this scenario:
Source |
Destination |
Service |
Action |
Comment |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Net_A Net_B GW_B |
GW_B Net_A |
H323 |
Accept |
Bidirectional calls |
To define an H.323 rule for a gateway in the external network:
For the example, these are Net_A and Net_B.
To define Hide NAT or Static NAT for the phones in the internal network, edit the network object for Net_A.
If you select Hide NAT:
If you use Hide NAT, add a Node object (with the Hide NAT IP address) to the Destination of the rules defined.
The image shows an H.323-based VoIP topology where a Gatekeeper is installed in the DMZ. This procedure explains how to:

VoIP rule for this scenario:
Source |
Destination |
Services & Applications |
Action |
Comments |
|---|---|---|---|---|
GK_DMZ Net_A Net_B |
Net_A Net_B GK_DMZ |
H323 H323_ras |
Accept |
Bidirectional calls. |
Static NAT rules for the Gatekeeper in the DMZ:
Original |
Translated |
Comments |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Source |
Destination |
Services & Applications |
Source |
Destination |
Services & Applications |
|
GK_DMZ |
Net_B |
*Any |
GK_DMZ: |
= |
= |
Outgoing calls |
Net_B |
GK_DMZ_NATed |
*Any |
= |
GK_DMZ: |
= |
Incoming calls |
To define an H.323 rule for a Gatekeeper in the DMZ:
In the image, these are Net_A and Net_B.
To define Hide NAT or Static NAT for the phones in the internal network, edit the network object for Net_A.
If you select Hide NAT:
You must associate the translated IP address with the MAC address of the gateway interface that is on the same network as the translated addresses. Use the arp command in UNIX or the local.arp file in Windows.
The command fw ctl arp displays the ARP proxy table on gateways that run on Windows. On UNIX, use the arp -a command.
H323_ras service greater or equal to the Gatekeeper registration time-out. The Inspection Settings window opens.
The image shows an H.323-based VoIP topology where a Gateway is installed in the DMZ. This procedure shows you how to:

VoIP rule for this scenario:
Source |
Destination |
Services & Applications |
Action |
Comments |
|---|---|---|---|---|
GW_DMZ Net_A Net_B |
Net_A Net_B GW_DMZ |
H323 |
Accept |
Bidirectional calls |
Static NAT rule for the Security Gateway in the DMZ:
Original |
Translated |
Comment |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Source |
Destination |
Services & Applications |
Source |
Destination |
Services & Applications |
|
GW_DMZ |
Net_B |
*Any |
GW_DMZ: |
= |
= |
Outgoing calls |
Net_B |
GW_DMZ_NATed |
*Any |
= |
GW_DMZ: |
= |
Incoming calls |
To define an H.323 rule for a gateway in the DMZ:
In the image, these are Net_A and Net_B.
To define Hide NAT or Static NAT for the phones in the internal network, edit the network object for Net_A.
If you select Hide NAT:
arp command in UNIX or the local.arp file in Windows.The command fw ctl arp displays the ARP proxy table on gateways that run on Windows. On UNIX, use the arp -a command.