Threat Emulation - Emulation environment
What can I do here?
Use this window to configure the Threat Emulation location and environment.

|
Getting Here - Security Policies > Threat Prevention > Policy > Threat Tools > Profiles > Profile > Threat Emulation > Emulation Environment
|
ThreatCloud Emulation
You can securely send files to the Check Point ThreatCloud for emulation. The ThreatCloud is always up-to-date with the latest Threat Emulation releases.
Sample ThreatCloud Emulation Workflow
- The Security Gateway gets a file from the Internet or an external network.
- The Security Gateway compares the cryptographic hash of the file with the database.
- If the file is already in the database, no additional emulation is necessary
- If the file is not in the database, it is necessary to run full emulation on the file
- The file is sent over an SSL connection to the ThreatCloud.
- The virtual computers in the ThreatCloud run emulation on the file.
- The emulation results are sent securely to the Security Gateway for the applicable action.
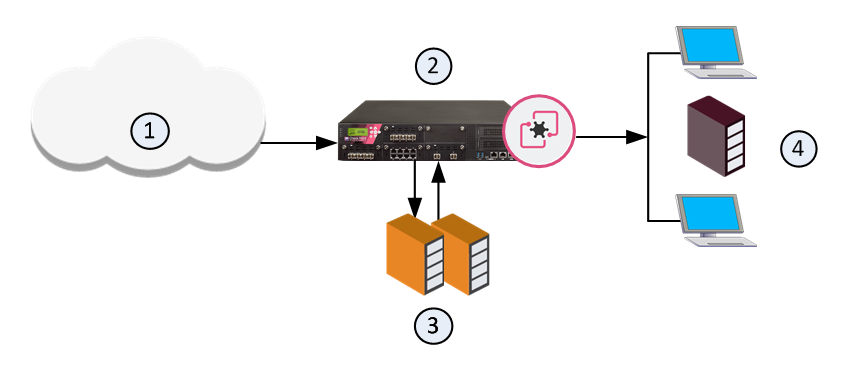
Sample ThreatCloud Deployment
Item
|
Description
|
1
|
Internet and external networks
|
2
|
Perimeter Security Gateway
|
3
|
Check Point ThreatCloud servers
|
4
|
Computers and servers in the internal network
|
Threat Emulation Analysis Locations
You can choose a location for the emulation analysis that best meets the requirements of your company.
- ThreatCloud - You can send all files to the Check Point ThreatCloud for emulation. Network bandwidth is used to send the files and there is a minimal performance impact on the Security Gateway.
- Threat Emulation Private Cloud Appliance (Emulation appliance) in the Internal network - You can use an Emulation appliance to run emulation on the files.
Local or Remote Emulation
You can install an Emulation appliance in the internal network.
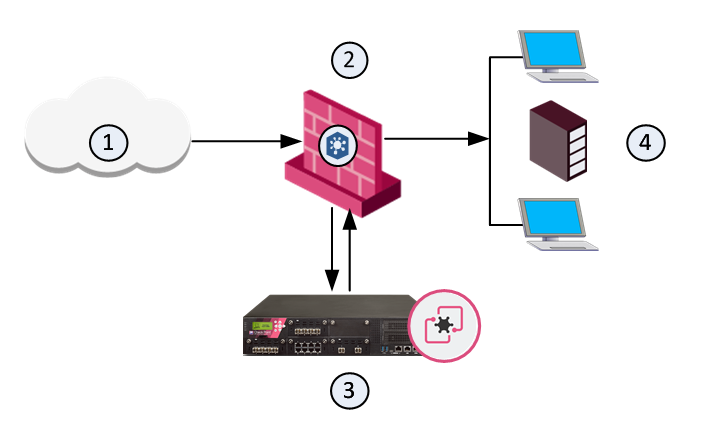
Sample Workflow for Emulation Appliance in a Local Deployment
- The Emulation appliance receives the traffic, and aggregates the files.
- The Emulation appliance compares the cryptographic hash of the file with the database.
- The file is already in the database, no more emulation is necessary.
- If the file is not in the database, the virtual computers in the Emulation appliance run full emulation on the file.
Item
|
Description
|
1
|
Internet and external networks
|
2
|
Perimeter Security Gateway
|
3
|
Threat Emulation Private Cloud Appliance
|
4
|
Computers and servers in the internal network
|
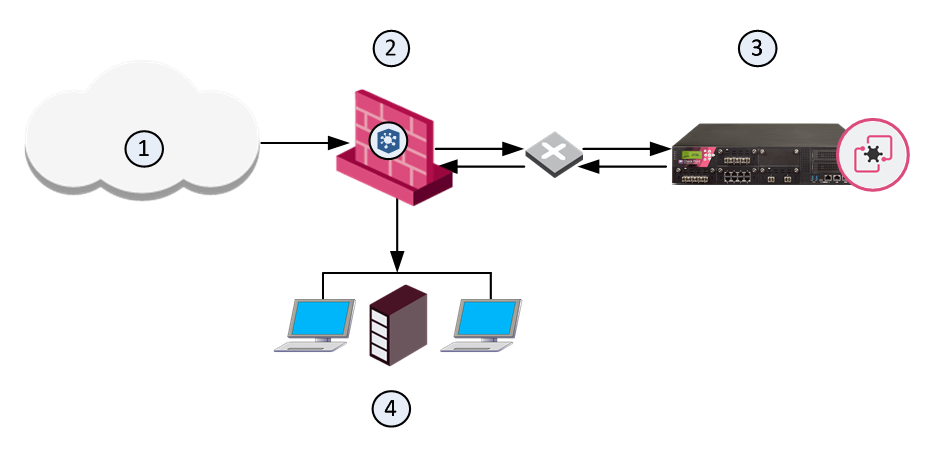
Sample Workflow for Emulation Appliance in a Remote Deployment
- The Security Gateway aggregates the files, and the files are sent to the Emulation appliance.
- The Emulation appliance compares the cryptographic hash of the file with the database.
- The file is already in the database, no more emulation is necessary.
- If the file is not in the database, the virtual computers in the Emulation appliance run full emulation on the file.
Item
|
Description
|
1
|
Internet and external networks
|
2
|
Perimeter Security Gateway
|
3
|
Threat Emulation Private Cloud Appliance
|
4
|
Computers and servers in the internal network
|
Optimizing File Emulation
Files have unique cryptographic hashes, these file hashes are stored in a database after emulation is complete. Before emulation is run on a file, the appliance compares the file hash to the database:
- If the hash is not in the database, the file is sent for full emulation
- If the hash is in the database, then it is not necessary to run additional emulation on the file
This database helps to optimize emulation and give better network performance.
Selecting the Threat Emulation Deployment
What are my options to send traffic for emulation?
- Inline - Traffic is sent for emulation before it is allowed to enter the internal network. You can use the Threat Prevention policy to block malware.
- SPAN/TAP - You can use a mirror or TAP port to duplicate network traffic. Files are sent to the computer in the internal network. If Threat Emulation discovers that a file contains malware, the appropriate log action is done.
- MTA (Mail Transfer Agent) - SMTP traffic goes to the Security Gateway, and is sent for emulation. The MTA acts as a mail proxy, and manages the SMTP connection with the source. The MTA sends email files to emulation after it closes the SMTP connection. When the file emulation is completed, the emails are sent to the mail server in the internal network. Best Practice - enable the MTA on the Security Gateway for Threat Emulation profiles that use the Prevent action for SMTP traffic.
- A Threat Emulation deployment that uses an MTA optimizes emulation for profiles that use the Prevent action.
I want to use the Prevent action and be able to block malicious files, what are my deployment options?
- ThreatCloud - Files are sent to the ThreatCloud for emulation. When the emulation is complete, ThreatCloud sends a notification to the Security Gateway that the files are safe. Then they go to computers in the internal network.
- Threat Emulation Private Cloud Appliance with inline deployment - The files are kept in the Emulation appliance and after emulation, safe files go to the computer in the internal network.
This table summarizes how Threat Emulation sends traffic for emulation:
|
Block Malware
|
Inline
|
Yes
|
SPAN/TAP
|
No
|
MTA
|
Recommended with Prevent action for emails
|
Inline Deployments (Prevent and Ask)
Use the Prevent or Ask UserCheck action to quarantine a malicious file.
Sample Inline Emulation Workflow (Prevent Action)
- The ThreatCloud or Emulation appliance gets a file from the Security Gateway.
- Emulation is run on the file.
- The file is safe, and it is sent to the computer in the internal network.
- If the file contains malware, it is quarantined and logged.
Monitor Deployments
Sample Monitor Emulation Workflow
- The ThreatCloud or Emulation appliance gets a copy of a file from the Security Gateway. The original file goes to the computer in the internal network.
- Emulation is run on the file.
- The file is safe, no other action is done
- If the file is identified as malware, it is logged according to the action of the Threat Prevention rule
Threat Emulation Deployments with a Mail Transfer Agent
Best Practice - If you use the Prevent action to block SMTP traffic, we recommend that you enable the Security Gateway as an MTA (Mail Transfer Agent). You can use the MTA to help manage the emulation of emails and attachments.
SMTP traffic goes to the Security Gateway, and is sent for emulation. The MTA acts as a mail proxy, and manages the SMTP connection with the source. The MTA sends email files to emulation after it closes the SMTP connection. When the file emulation is completed, the emails are sent to the mail server in the internal network.
Check Point ThreatCloud Network
By default, all gateways send threat information to the ThreatCloud.
You can change this default behavior in SmartConsole.
To configure all gateways not to send information to the ThreatCloud:
- Open .
- In the area, clear this setting: .
- Click .
- Restart SmartConsole.
- .
System Specifications
These are the specifications for the Threat Emulation deployments:
- Threat Cloud - R77 (or higher) Security Gateways with Gaia or SecurePlatform (64 or 32-bit)
- R77.20 (or higher) VSX Gateways
- For Local or Remote emulation:
Maximum size of file to send to emulation is: 100,000 KB
Check Point Threat Emulation Private Cloud Appliance with R77 or higher on the Gaia operating system (64-bit only), and R77.20 or higher VSX Gateways (Remote emulation only)
Make sure that:
- Each Virtual System has access to the Remote gateway or to the cloud.
- Each Virtual System Gateway has access to the Internet for updates from the Check Point Download Center.
Note - This release does not support:
- Active/Standby Bridge Mode
- Virtual System Load Sharing Security Clusters with more than two members.
- MTA