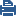


If you have a ClusterXL Cluster, connect each cluster member to both ISPs via a LAN using two interfaces. The cluster-specific configuration is illustrated below.
Note that the member interfaces must be on the same subnet as the cluster external interfaces. Configure ClusterXL in the usual way.
ClusterXL supports Dynamic Routing (Unicast and Multicast) protocols as an integral part of SecurePlatform. As the network infrastructure views the clustered Security Gateway as a single logical entity, failure of a cluster member will be transparent to the network infrastructure and will not result in a ripple effect.
Important - When you use any of the Advanced Routing protocols, enable the Wait for Clustering option on the Gaia UI. See sk92322.
All cluster members use the cluster IP address(es).
Routing information is synchronized among the cluster members using the Forwarding Information Base (FIB) Manager process. This is done to prevent traffic interruption in case of failover, and used for Load Sharing and High Availability modes. The FIB Manager is the responsible for the routing information.
The FIB Manager is registered as a critical device (Pnote), and if the slave goes out of sync, a Pnote will be issued, and the slave member will go down until the FIB Manager is synchronized.
Dynamic Routing on ClusterXL avoids creating a ripple effect upon failover by informing the neighboring routers that the router has exited a maintenance mode. The neighboring routers then reestablish their relationships to the cluster, without informing the other routers in the network. These restart protocols are widely adopted by all major networking vendors. The following table lists the RFC and drafts compliant with Check Point Dynamic Routing:
Protocol |
RFC or Draft |
|---|---|
OSPF LLS |
draft-ietf-ospf-lls-00 |
OSPF Graceful restart |
RFC 3623 |
BGP Graceful restart |
draft-ietf-idr-restart-08 |
The components listed above function "behind-the-scenes." When configuring Dynamic Routing on ClusterXL, the routing protocols automatically relate to the cluster as they would to a single device.
When configuring the routing protocols on each cluster member, each member is defined identically, and uses the cluster IP address(es) (not the member physical IP address). In the case of OSPF, the router ID must be defined and identical on each cluster member. When configuring OSPF restart, you must define the restart type as signaled or graceful. For Cisco devices, use type signaled.
Use the SecurePlatform command line to configure each cluster member.
--------- Launch the Dynamic Routing Module [Expert@GWa]# router localhost>enable localhost#configure terminal --------- Enable OSPF and provide an OSPF router ID localhost(config)#router ospf 1 localhost(config-router-ospf)#router-id 192.168.116.10 localhost(config-router-ospf)#restart-type [graceful | signaled] localhost(config-router-ospf)#redistribute kernel --------- Define interfaces/IP addresses on which OSPF runs (Use the cluster IP address as defined in topology) and the area ID for the interface/IP address localhost(config-router-ospf)#network 1.1.10.10 0.0.0.0 area 0.0.0.0 localhost(config-router-ospf)#network 1.1.10.20 0.0.0.0 area 0.0.0.0 -------- Exit the Dynamic Routing Module localhost(config-router-ospf)#exit localhost(config)#exit -------- Write configuration to disk localhost#write memory IU0 999 Configuration written to '/etc/gated.ami' |
The same configuration needs to be applied to each cluster member.
As the FIB Manager uses TCP 2010 for routing information synchronization, the Security Policy must accept all traffic on port TCP 2010 between cluster members.
For detailed information regarding Dynamic Routing, see the R77 Advanced Routing Suite CLI Reference guide.