Configuring Check Point Redundant IPsec Tunnel
This topic explains how to establish a single Site-to-Site tunnel between your Harmony SASE Network and Check Point Firewall.
Pre-requisites
-
Harmony SASE Administrator Portal account.
-
Device with Harmony SASE Agent installed.
-
Administrator account with Firewall, Router, and Cloud Management Portal.
-
A cluster of two Quantum gateways, each with a public IP.
-
Configuration with ISP redundancy PMTR-68991 is not supported.
Part 1 - Configuration in SmartConsole
Step 1: Creating Interoperable Device Object in the Check Point SmartConsole
-
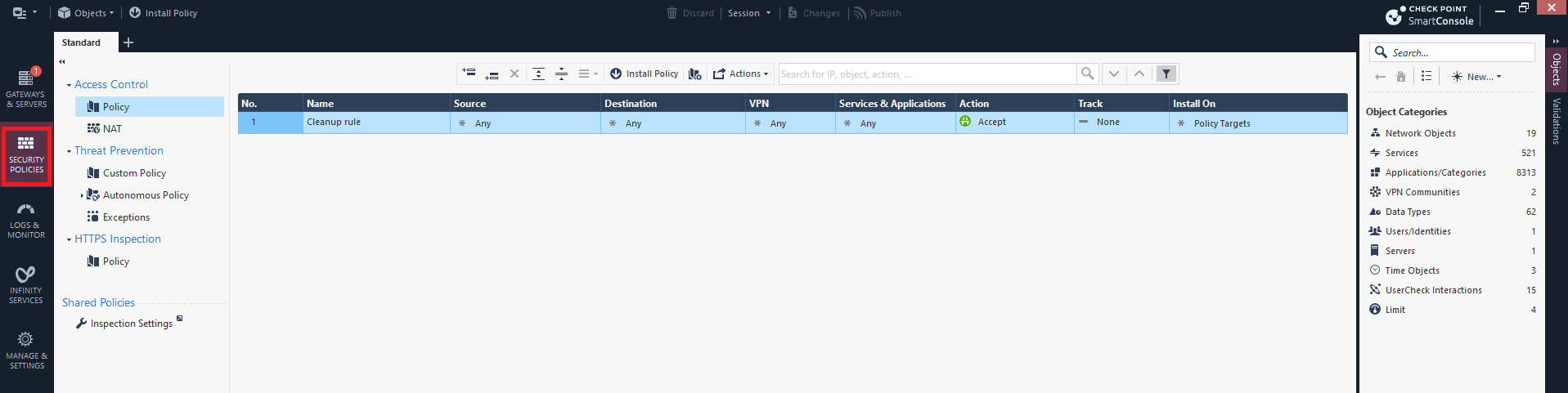
Log in to the Check Point SmartConsole.
-
Click Security Policies.
-
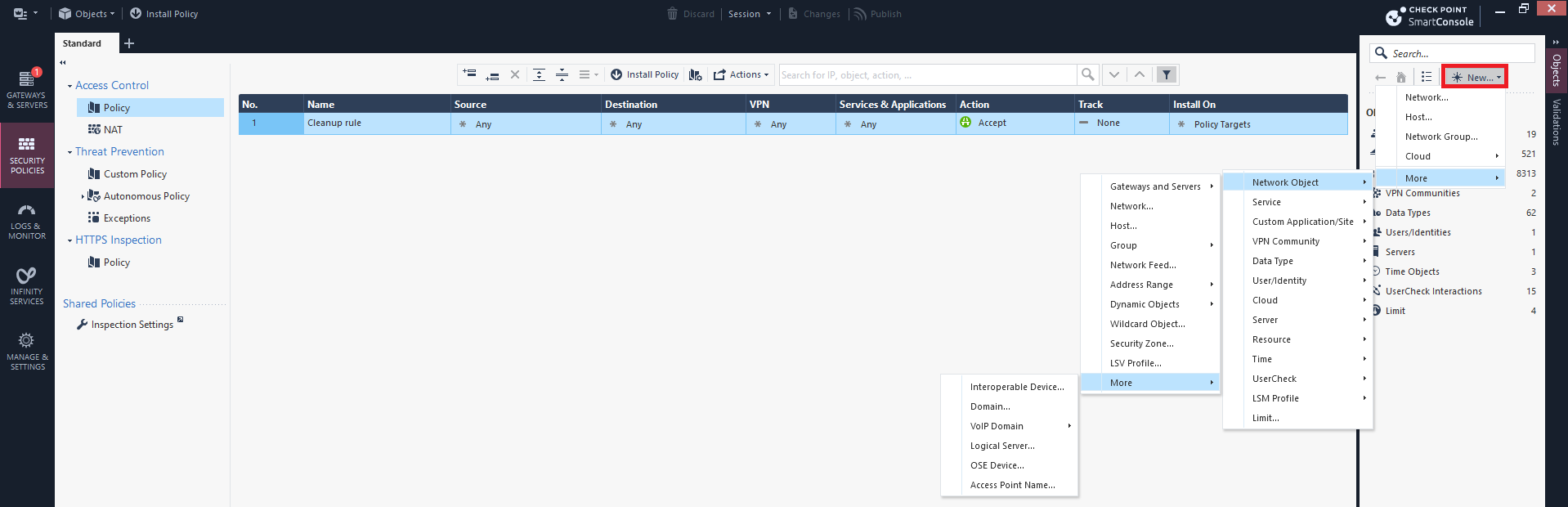
In the Objects pane, click New and select More > Network Object > More > Interoperable Device.
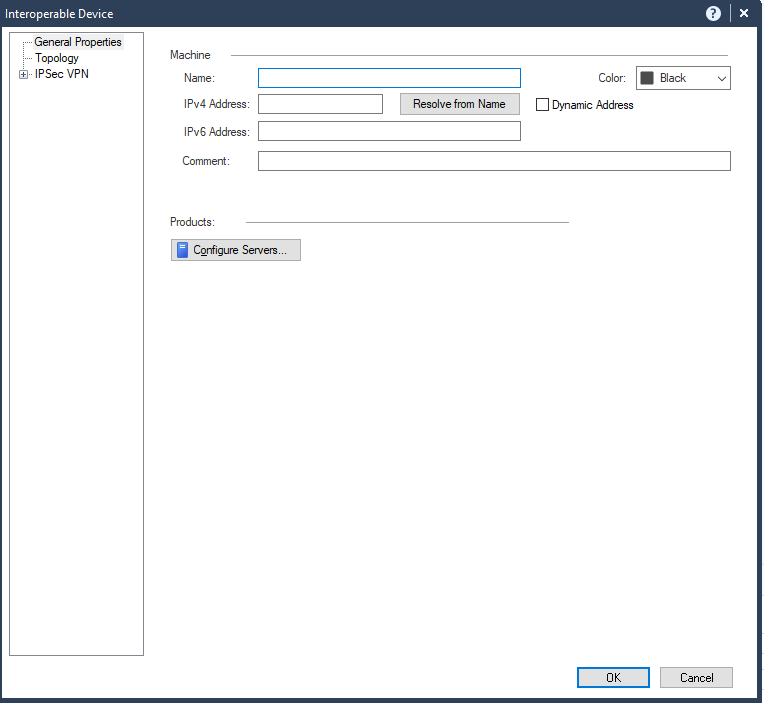
The Interoperable Device window appears.
-
In the Name field, enter a name for the Harmony SASE gateway, for example, Harmony_SASE_Gateway.
-
In the IPv4 Address field, enter the Harmony SASE gateway public IP address.
To find the Harmony SASE Gateway public IP Address:
-
Access the Harmony SASE Administrator Portal and click Networks.
-
Select the network.
-
Go to the Gateways section to find the Public IP address for setting up the single IPsec tunnel.
-
-
Click OK.
-
Click
 on the left top corner of the page.
on the left top corner of the page. -
Select Global properties.
-
Go to VPN > Advanced.
-
Select the Enable VPN Directional Match in VPN Column checkbox.
-
Click OK.
-
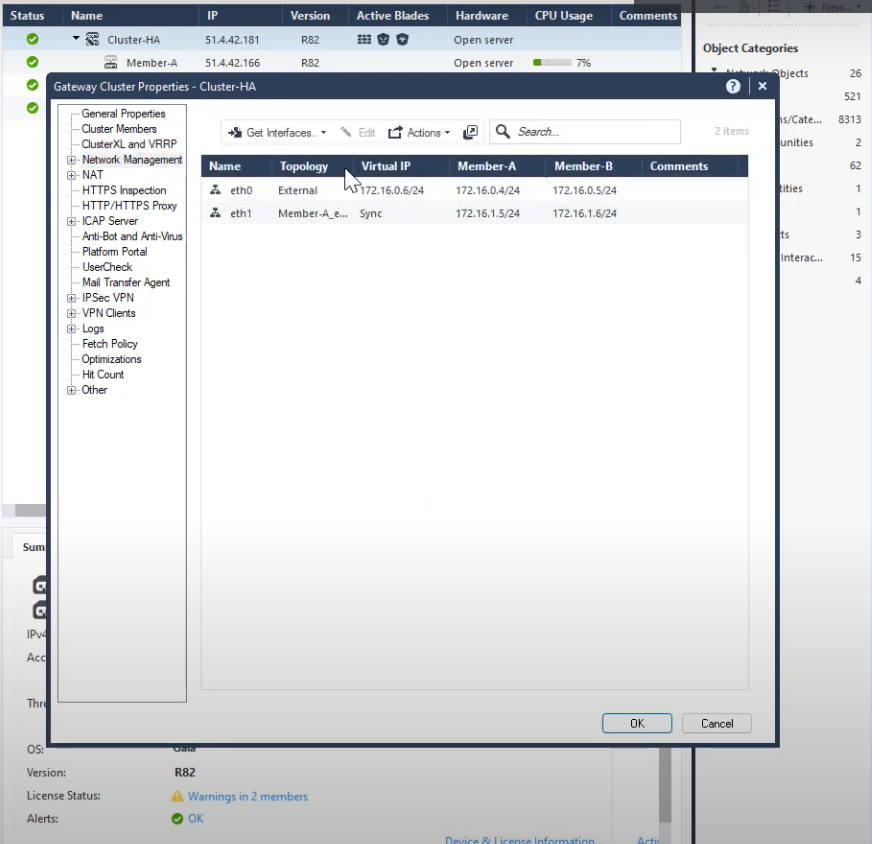
Select the cluster from the table.
-
Click General Properties.
-
Select the IPSec VPN checkbox.
-
Click Network Management.
-
Click Get Interfaces.
-
Select Get Interfaces With Topology.
The SmartConsole window appears.
-
Click Yes.
-
Double-click the Cluster Member 1.
-
In the IPv4 Address field, enter the Harmony SASE gateway public IP address.
To find the Harmony SASE Gateway public IP Address:
-
Access the Harmony SASEAdministrator Portal and click Networks.
-
Select the network.
-
Go to the Gateways section to find the Public IP address for setting up the single IPsec tunnel.
-
-
Click Modify.
-
In the Anti-Spoofing section, unselect the Perform Anti-Spoofing based on interface topology checkbox.
-
Click OK.
-
Click OK.
-
Repeat step from p through u for Cluster Member 2.
-
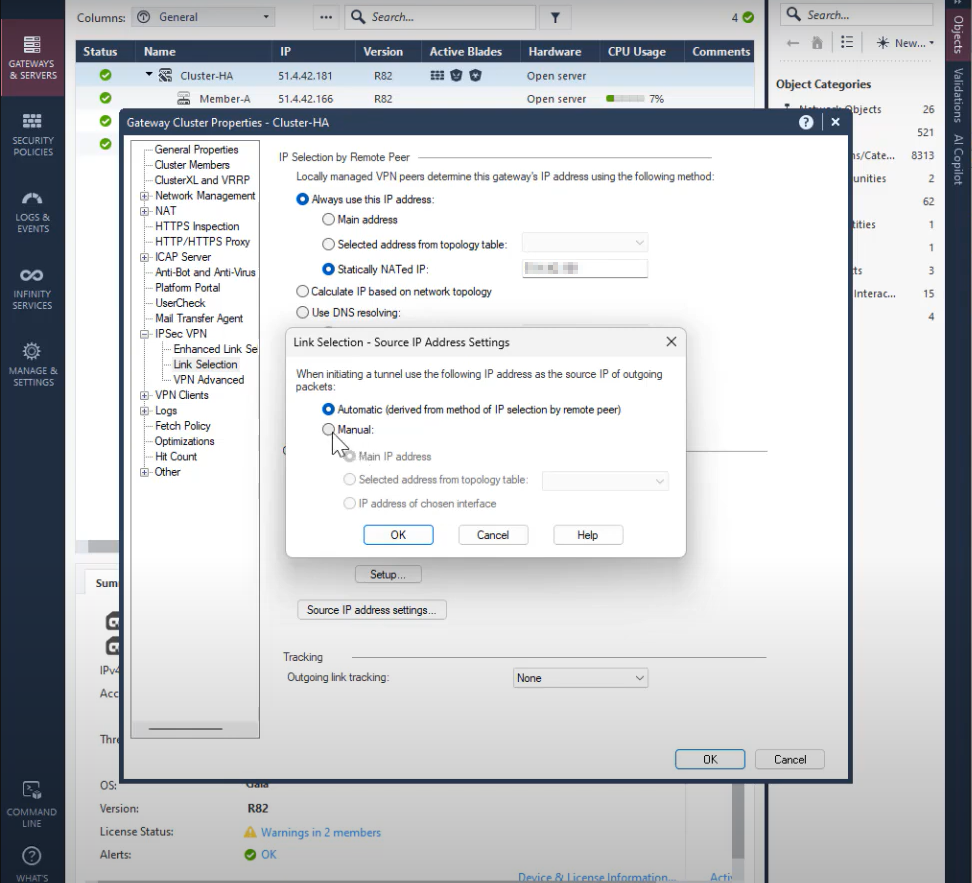
Go to IPSec VPN > Link Selection.
-
Select the Statically NATed IP checkbox and enter the Harmony SASE gateway public IP address.
-
Click Source IP address settings.
The Link Selection - Source IP Address Settings window appears.
-
Select Manual and then select Selected address from topology table checkbox.
-
From the list, select the private IP address.
-
Click OK.
-
Click OK.
-
Publish and install the policy.
-
Step 2: Adding Harmony SASE Gateway IP Address and Remote Subnet To The Interoperable Device Object
-
Log in to the Harmony SASE Administrator Portal.
-
Click Networks.
-
Verify the assigned network:
-
Select a network, scroll to the end of the row and click
 .
. -
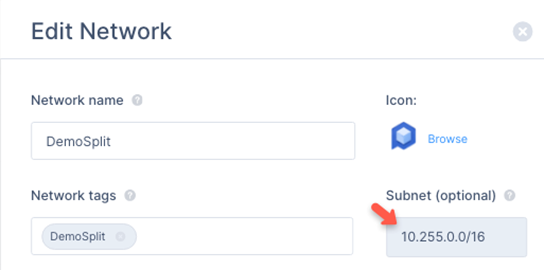
Select Edit Network.
-
In the Edit Network section, check the Subnet field to verify the assigned network. The default value is 10.255.0.0/16.
-
-
Open the network object that you created.
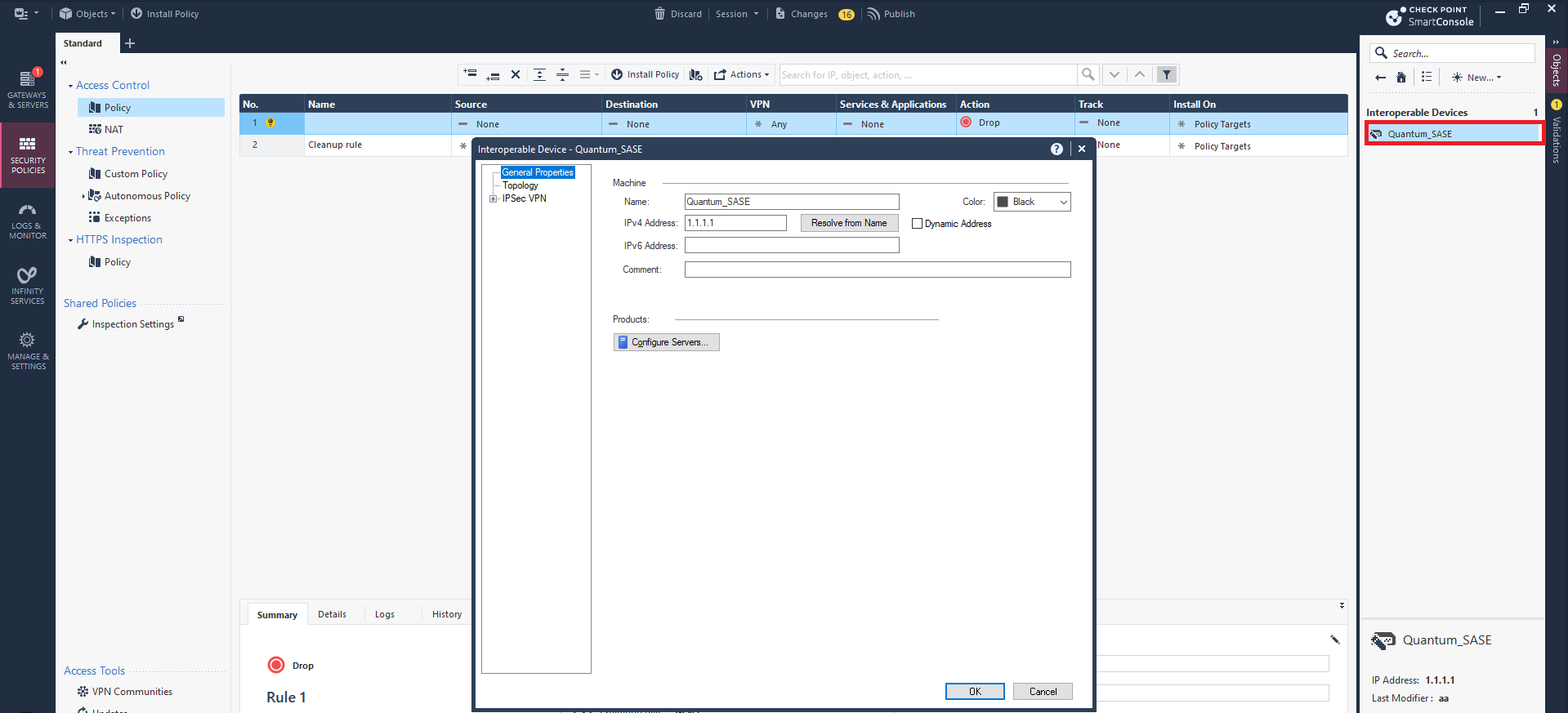

Note - If the gateway is configured with an interface topology that includes a network range or a group overlapping with the encryption domain of the remote VPN peer, incoming decrypted traffic may be seen as coming from the wrong interface. This could trigger anti-spoofing measures, causing traffic to be dropped. To create an anti-spoofing exception, see sk151774.
-
Click Topology > New.
-
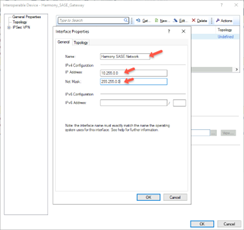
In the General tab:
Field
Enter
Name Name for the topology. IP Address
10.255.0.0 Net Mask 255.255.0.0 -
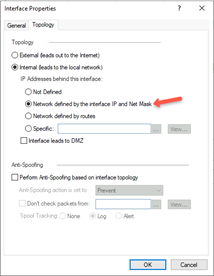
In the Topology tab, select Internal (leads to the local network) and select Network defined by the interface IP and Net Mask.
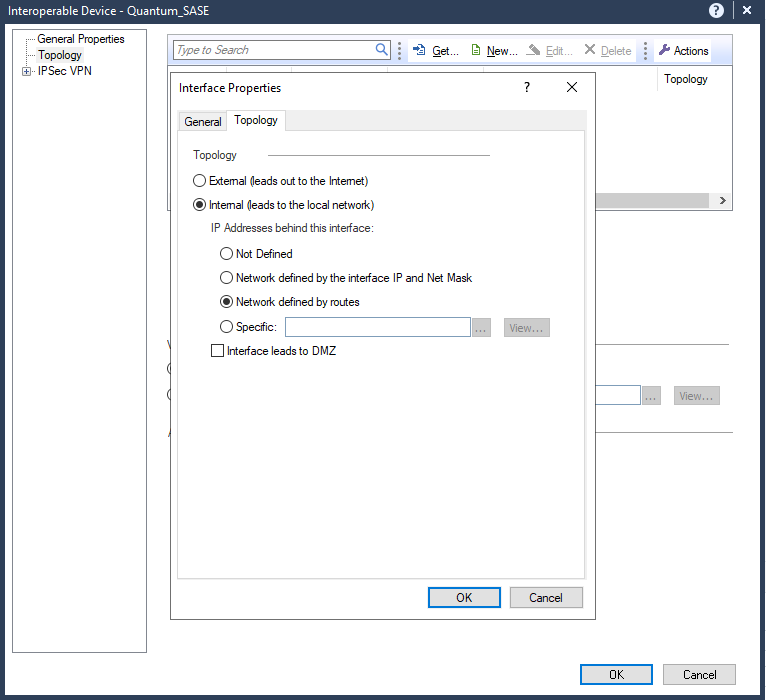
-
Click OK.
-
Click Topology > New.
-
In the General tab:
Field
Enter
Name Name for the topology. IP Address
Public IP address of the Harmony SASE gateway. Net Mask 255.255.255.255 -
In the Topology tab, select External (leads to the local Internet).
-
Click OK.
-
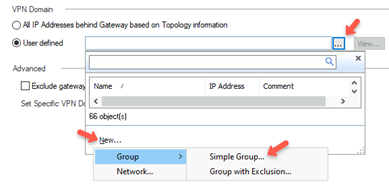
In the VPN Domain section, select User defined and click
 .
. -
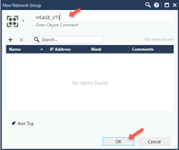
Click New and go to Group > Simple Group.
The New Network Group window appears.
-
In the Enter Object Comment field, enter a name, for example, HSASE_VTI, and click OK.
-
For the other Harmony SASE Gateway and Check Point Gateway, follow the same procedure in Creating Interoperable Device Objects in the Check Point SmartConsole and Adding Harmony SASE Gateway IP Address and Remote Subnet To The Interoperable Device Object sections.
-
Publish and install the policy.
Step 3: Creating VPN Start Community
-
Log in to the Check Point SmartConsole.
-
Click Security Policies.
-
Go to Access Tools > VPN Communities.
-
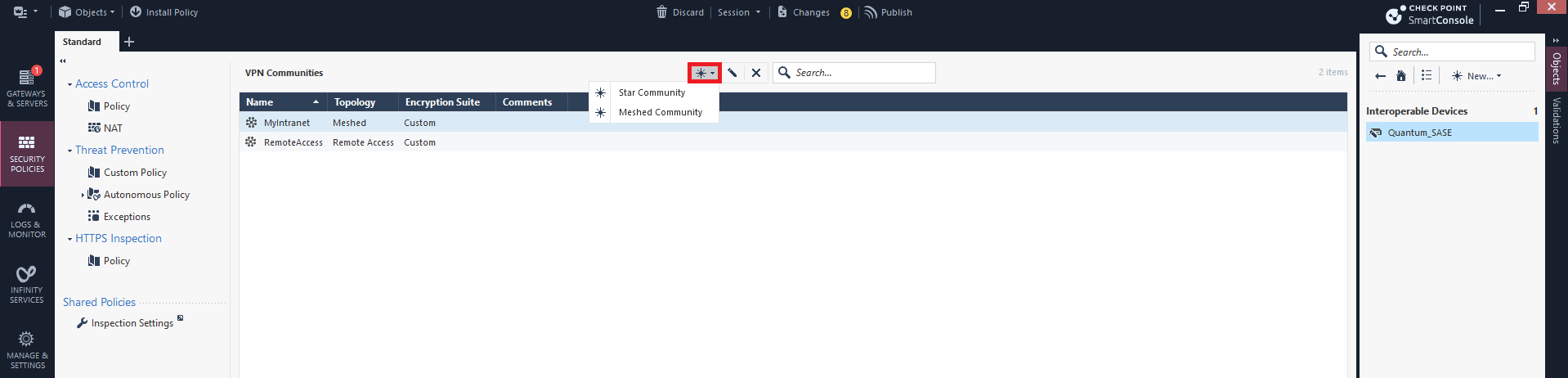
Select an object, click New and go to More > VPN Community > Star Community.
The New Star Community window appears.
-
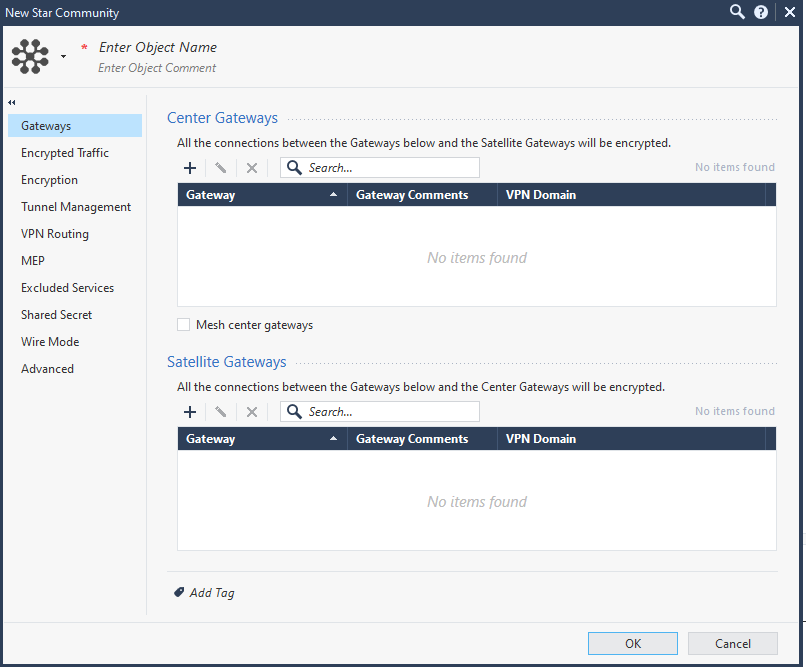
In the Enter Object Name field, enter an object name for the VPN Start Community, for example, Harmony_SASE_VPN.
-
In the Link Selection Mode section, select one of these:
-
Enhanced (Recommended) - Uses dynamic, intelligent, probe-based logic to choose the optimal VPN link. It evaluates:
-
Interface status
-
Multiple external IP addresses
-
Multiple ISP circuits
-
Reachability through Next-Hop Probing
-
SLA-like behavior for tunnel selection
-
-
Legacy - Uses static or basic logic to select the VPN interface or IP address. Selection is based on:
-
Main IP (default)
-
Selected interface
-
Selected IP
-
IP address determined by topology
-
-
-
Under Center Gateways, click
and add the Check Point Gateway:
The cluster is added to the table.
-
Double-click the cluster in the table.
-
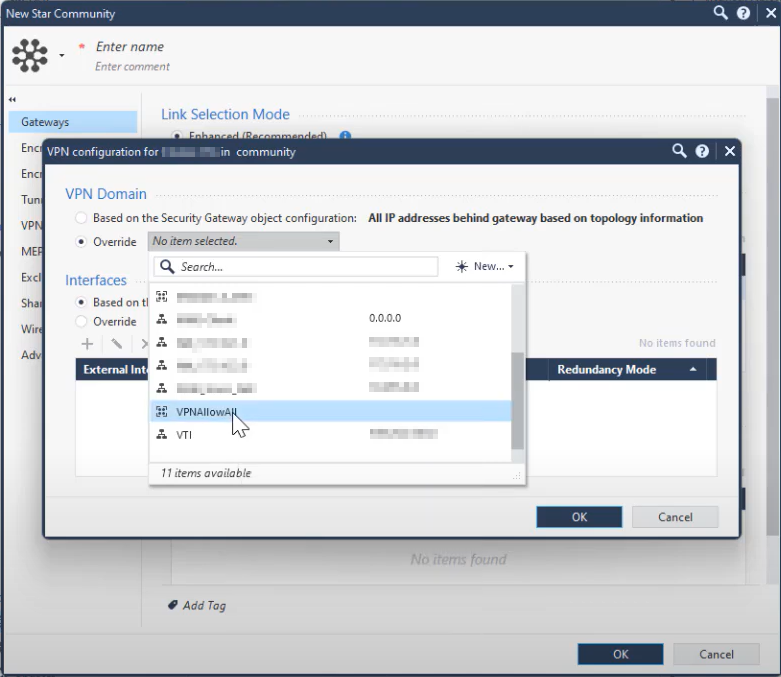
In the VPN Domain section, select the Override checkbox and from the list, select the allow all VPN group.
-
In the Interfaces section, select the Override checkbox and click
.
The Interface Settings window appears.
-
Specify these:
-
External Interface
-
Static NAT IP Address - The Harmony SASE gateway public IP address.
-
-
Click OK.
-
Click OK.
-
-
Under Satellite Gateways, click
and add the Interoperable Device Object created for the Check Point Gateway. See Step 1.
-
From the table, double-click the cluster of the first Quantum Gateway.
-
In the VPN Domain section, select the Override checkbox and from the list, select the allow all VPN group.
-
In the Interfaces section, select the Override checkbox and click
.
The Interface Settings window appears.
-
Specify these:
-
External Interface
-
Static NAT IP Address - The Harmony SASE gateway public IP address.
-
-
Click OK.
-
Click OK.
-
Repeat the steps from a through f for the cluster of the second QuantumGateway.
-
-
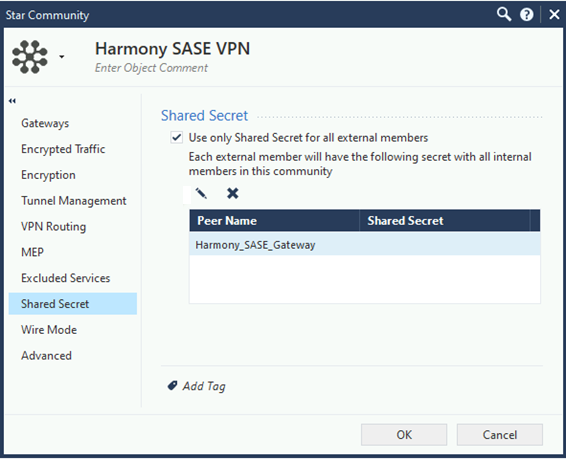
Go to Shared Secret and click
 to edit the shared key.
to edit the shared key. -
In the Enter secret field, enter an appropriate key.

Notes:
-
Copy the key as it is required while configuring the IPsec Tunnel in the Harmony SASE Administrator Portal.
-
Check Point recommends that the share secret key is at least 20 characters in length.
-
-
Click OK.
-
From the left navigation pane, click Encryption and do these:
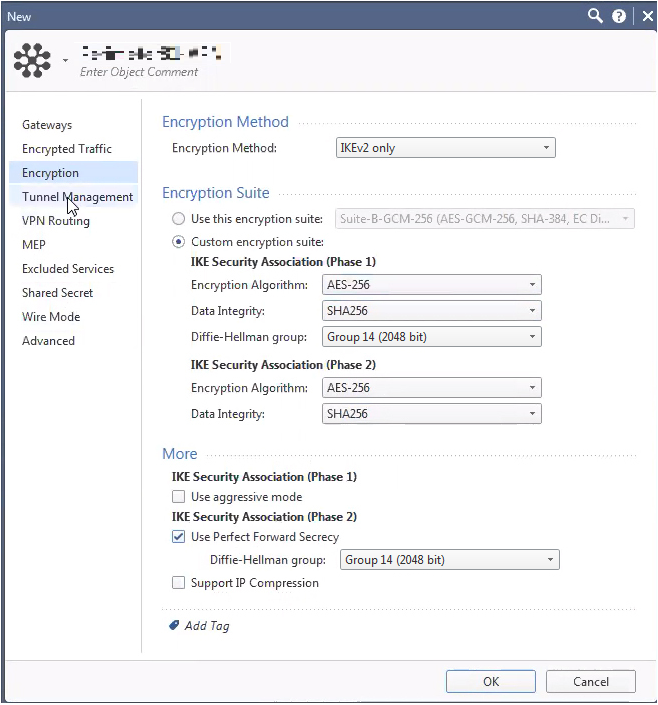
Field
Enter
Encryption Method IKEv2 only Custom encryption suite IKE Security Association (Phase 1)
Encryption Algorithm AES-256 Data Integrity SHA256 Diffie Hellman group Group 14 (2048 bit) IKE Security Association (Phase 2)
Encryption Algorithm AES-256 Data Integrity SHA256 More
IKE Security Association (Phase 2)
Use Perfect Forward Secrecy
Diffie Hellman group Group 14 (2048 bit) -
Click Tunnel Management.
-
In the Permanent Tunnels section, select the Set Permanent Tunnels checkbox and then select On all tunnels in the community.
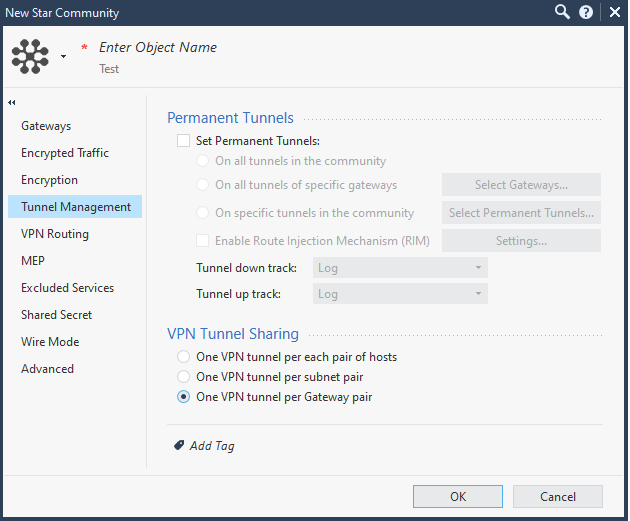
-
In the VPN Tunnel Sharing section, select One VPN tunnel per Gateway pair.

Important - Make sure that you enter the remote subnets specified here in the Harmony SASEAdministrator Portal. A mismatch can disconnect the tunnel.
-
Click Advanced.
-
In the IKE (Phase 1) section, set the Renegotiate IKE security associations every (minutes) field to 480.
-
In the IPsec (Phase 2) section, set the Renegotiate IPsec security associations every (seconds) field to 3600.
-
-
In the Properties section, select the Disable NAT inside the VPN community checkbox and from the list, select Both center and satellite gateways.
-
Click OK.
-
Repeat steps 1 to 17 for the other Check Point Gateway and Harmony SASE Gateway.
-
Publish and install the policy.
Step 4: Additional settings in Check Point SmartConsole
-
To set up a Check Point firewall policy, add a rule for VPN traffic for the specific VPN Domain in the Check Point SmartConsole.
In the example below, we have created a policy to allow traffic from the Harmony SASE Network 10.255.0.0/16 to specific destinations and services. Note that the network configuration may differ if you have not changed the default settings during Harmony SASE network creation. For testing purposes, you should initially allow any/any or allow before making the firewall policy more restrictive.

Note - The network configuration differs if you have not changed the default settings during Harmony SASE network creation. For testing purposes, you should initially allow any/any or allow ping before making the firewall policy more restrictive.
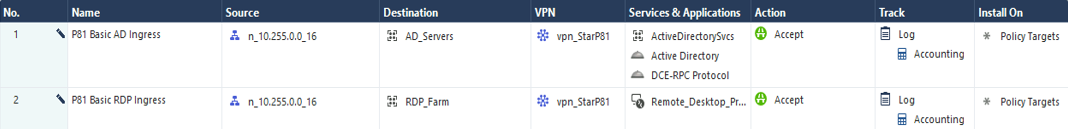
-
Publish and install the policy.
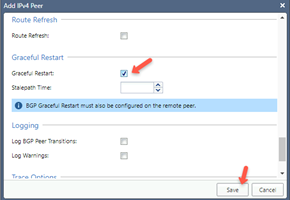
Step 5: Configuring VPN Tunnel Interface and BGP Configuration
-
Log in to the Check Point Gaia Portal of the first Check Point Gateway.
-
Click Network Interfaces.
-
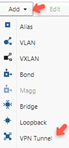
From the Add list, select VPN Tunnel.
The Add VPN Tunnel page appears.
-
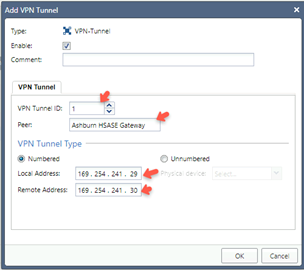
Enter these:
-
VPN Tunnel ID - Select a unique ID.
-
Peer - Name of the interoperable device previously created for the first Harmony SASE Gateway.
-
VPN Tunnel Type - Numbered.
-
Local Address - Internal address for the Quantum Gateway (within 169.254.x.x/30 ranges).
-
Remote Address - Internal address for the Harmony SASE Gateway (within 169.254.x.x/30 ranges, corresponding to the above).
-
-
Click OK.
-
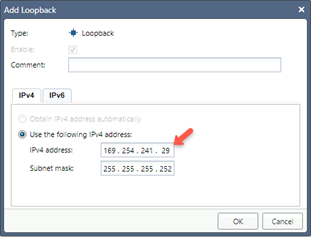
Click Network Interfaces, Add > Loopback.
-
Select Use the following IPV4 address.
-
In the IPv4 field, enter the Local Address entered in step 4 and click OK.
-
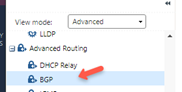
Go to Advanced Routing and select BGP.
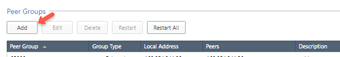
-
In the Peer Groups section, click Add.
-
Enter these:
-
Peer AS Number - The AS Number of the Harmony SASE network. If not set already, enter 64512.
-
Peer Group Type - External.
-
Local Address - The local address entered in the VTI configuration section Step 4.
-
-
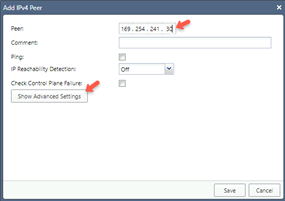
Click Add Peers.
-
Enter these:
-
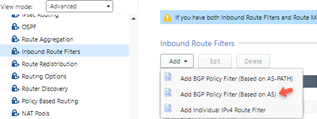
From the View mode list, select Advanced Routing and click Inbound Route Filter.
-
From the Add list, select Add BGP Policy Filter (Based on AS).
The Add BGP Policy Filter based on AS window appears.
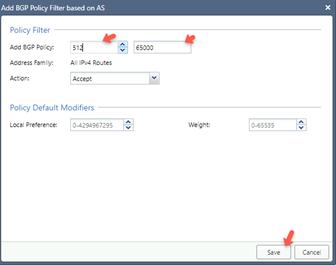
-
Specify these:
-
Add BGP Policy - Set a number from the available range.
-
AS Number - Set the AS Number of the Harmony SASE Network.
-
Action - Accept
-
-
Click Save.
-
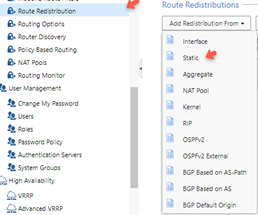
From the View mode list, select Advanced Routing, click Route Redistribution.
-
From the list, select Add Redistribution From.
-
Select Static.

Note - For BGP, no routes are accepted from a peer by default. You must configure an explicit Inbound BGP Route Filter to accept a BGP route from a peer.
-
Repeat the steps for the second Check Point Gateway and Harmony SASE Gateway. Use a different 169.254.x.x/30 range for the local and remote peer IP addresses.
Part 2 - Configuration in Harmony SASE Administrator Portal
Step 1: Configuring Tunnel and Routes Table
-
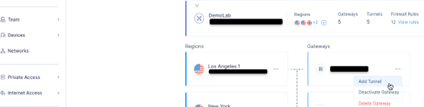
Access the Harmony SASE Administrator Portal and click Networks.
-
Select the network.
-
Click
 .
. -
Select Add Tunnel for the gateway from which you want to add the IPSec Site-2-Site VPN tunnel.
-
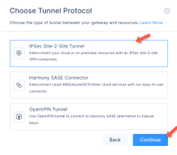
Click IPSec Site-2-Site Tunnel and click Continue.
-
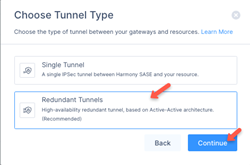
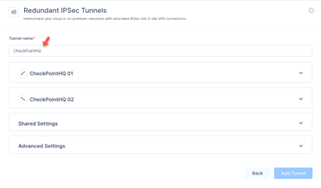
Click Redundant Tunnels and click Continue.
-
In the Tunnel name field, enter a logical name.
-
Expand Tunnel 1 and specify these:
-
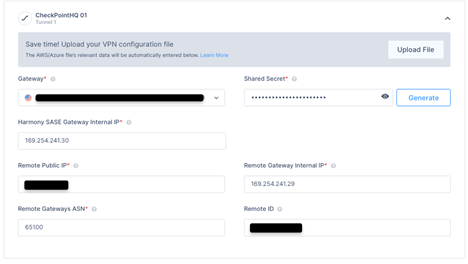
Shared Secret - The value previously set on the first start policy.
-
Harmony SASE Gateway Internal IP - The remote address of the first Check Point Gateway used under the VTI settings.
-
Remote Public IP - The public IP of the first Quantum Gateway.
-
Remote Gateway Internal IP - The local address of the first Quantum Gateway used under the VTI settings.
-
Remote Gateways ASN - The ASN of the first Quantum Gateway.
-
Remote ID - The router ID of the first Quantum Gateway used under the BGP settings above.
-
-
Expand Tunnel 2 and specify these:
-
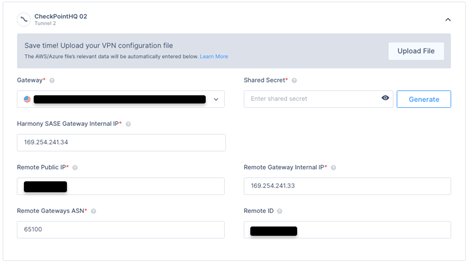
Gateway - Select the second Harmony SASE Gateway for the tunnel.
-
Shared Secret - The value previously set on the second star policy.
-
Harmony SASE Gateway Internal IP - The remote address of the second Quantum Gateway used under the VTI settings.
-
Remote Public IP - The public IP of the second Quantum Gateway.
-
Remote Gateway Internal IP -The local address of the second Quantum Gateway used under the VTI settings.
-
Remote Gateways ASN - The ASN of the second Quantum Gateway.
-
Remote ID - The router ID of the second Quantum Gateway used under the BGP settings above.
-
-
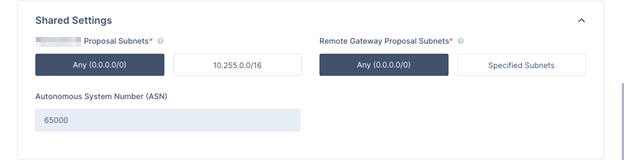
Expand Shared Settings and specify these:
-
Harmony SASE Gateway Proposal Subnets - Leave Any (0.0.0.0/0) selected.
-
Remote Gateway Proposal Subnets - Leave Any (0.0.0.0/0) selected.
-
Autonomous System Number (ASN) - Default value is 64512, if not set, enter the AS Number for the Harmony SASE network.
-
-
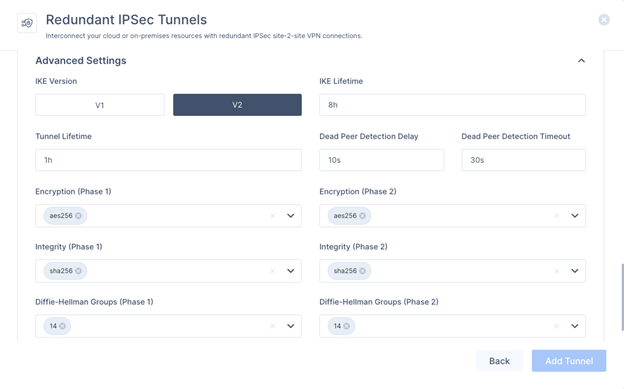
In the Advanced Settings section, specify these:
-
IKE Version: V2
-
IKE Lifetime: 8h
-
Tunnel Lifetime: 1h
-
Dead Peer Detection Delay: 10s
-
Dead Peer Detection Timeout: 30s
-
Phase 1:
-
Encryption(Phase 1): aes256
-
Integrity (Phase 1): sha256
-
Key Exchange Method: modp2048
-
-
Phase 2:
-
Encryption(Phase 2): aes256
-
Integrity (Phase 2): sha256
-
Key Exchange Method: modp2048
-
-
-
Click Add Tunnel.
-
-
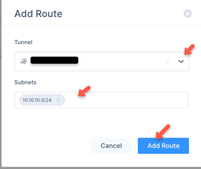
Select Routes Table:
Step 2: Verifying the Setup
Once you complete the above steps, your tunnel should be active.
-
Verify the setup in the Harmony SASE Administrator Portal:
-
Click Networks.
-
Locate the tunnel you create, and check the tunnel status.
It should indicate that the tunnel is Up, signifying a successful connection.
-
-
Verify the setup in the Harmony SASE Agent:
-
Connect to your network using the Harmony SASE Agent.
-
Access one of the resources in your environment.
-