Threat Prevention Policy
Threat Prevention is a security solution that protects your workspace from advanced threats.
This topic explains how to configure and manage the Threat Prevention policy to secure your organization against cyber risks.
Threat Prevention extends the Secure Web Gateway capabilities in Harmony SASE, offering advanced protection against cyber threats. It integrates three key security technologies:
-
Malware Protection: Scans files, downloads, and web content to detect and block malicious code before it infects your systems. It uses advanced detection engines to identify known malware signatures and suspicious behavior.
-
Threat Emulation: Leverages sandboxing technology to analyze suspicious files in a controlled environment. This detects zero-day threats and advanced attacks that may bypass traditional defenses by analyzing files for malicious behavior without affecting your production systems.
-
Anti-Bot: Protects users by blocking access to malicious websites and preventing communication with command-and-control servers. It assesses website reputation and prevents infected devices from reaching harmful servers.
The integration of these three technologies creates multiple layers of protection against various attack vectors:
-
Pre-execution Protection: Blocks known threats before execution.
-
Behavioral Analysis: Monitors file behavior in the sandbox to detect suspicious activities.
-
Post-infection Control: Stops infected devices from communicating with malicious servers.
This multi-layered approach significantly enhances your security posture by addressing threats at different stages of the attack lifecycle.
Threat Prevention Components
To challenge today's malware landscape, Threat Prevention solution offers a multi-layered, pre- and post-infection defence approach and a consolidated platform that enables enterprise security to detect and block modern malware.
These Threat Prevention protections are available:
-
Malware Protection - Pre-infection detection and blocking of malware at the gateway. The Anti-Virus protection is continuously updated from ThreatCloud. It detects and blocks malware by correlating multiple detection engines before users are affected.
-
Threat Emulation - Each protection is unique. When combined, they supply a strong Threat Prevention solution. Data from malicious attacks are shared between the Threat Prevention protections and help to keep your network safe. For example, the signatures from threats that Threat Emulation identifies are added to the ThreatCloud for use by the other Threat Prevention protections.
-
Anti-Bot - Prevents damage by blocking communication with dangerous URLs, particularly command-and-control servers for malicious bots. Anti-Bot is continuously updated from ThreatCloud, an AI-powered collaborative, distributed defense network and database to fight security threats.
Malware Protection
Malware is a major threat to network operations that has become increasingly dangerous and sophisticated. Examples include worms, blended threats (combinations of malicious code and vulnerabilities for infection and dissemination) and trojans.
The Malware protection scans incoming and outgoing files to detect and prevent these threats, and provides pre-infection protection from threats contained in these files. The Malware protection is also supported by the Threat Prevention API.
The Malware protection:
-
Identifies malware in the organization using the ThreatSpect engine and ThreatCloud repository:
-
Prevents malware infections from incoming malicious files types (Word, Excel, PowerPoint, PDF, etc.) in real-time. Incoming files are classified on the gateway and the result is then sent to the ThreatCloud repository for comparison against known malicious files, with almost no impact on performance.
-
Prevents malware download from the internet by preventing access to sites that are known to be connected to malware. Accessed URLs are checked by the gateway caching mechanisms or sent to the ThreatCloud repository to determine if they are permissible or not. If not, the attempt is stopped before any damage can take place.
-
-
Uses the ThreatCloud repository to receive binary signature updates and query the repository for Anti-Bot and malware protection classification.
Threat Emulation
Threat Emulation gives networks the necessary protection against unknown threats in web downloads. The Threat Emulation engine picks up malware at the exploit phase, before it enters the network. It quickly quarantines and runs the files in a virtual sandbox, which imitates a standard operating system, to discover malicious behavior before hackers can apply evasion techniques to bypass the sandbox.
Threat Emulation receives files through these methods of delivery
-
Web downloads
-
Files sent to Threat Emulation through the Threat Prevention API
When emulation is done on a file, it is observed for malicious behavior in a cloud-based security sandbox.
If the file is found to be not malicious, you can download the file after the emulation is complete.
Anti-Bot
A bot is malicious software that can infect your computer. It is possible to infect a computer when you open attachments that exploit a vulnerability or go to a web site that results in a malicious download.
When a bot infects a computer, it connects to a command-and-control server where it receives instructions to carry out malicious tasks.
One bot can often create multiple threats. Bots are frequently used as part of Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs) where cyber criminals try to damage individuals or organizations.
Our Anti-Bot mechanism prevents bots from communicating with their command-and-control servers, which reduces their threat significantly.
After the discovery of a communication attempt, Harmony SASE blocks outbound communication to C&C sites based on the Rule Base. This neutralizes the threat and prevents sensitive information from being sent out.
Risk Calculation
Threat Prevention uses a risk-based approach with values from 0-100, which simplifies threat assessment through a single interpretable value:
|
Risk Range |
Description |
Confidence |
Severity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Risk = 0 | Indications of a legitimate website | High | N/A |
| 0 < Risk < 10 | Internet long tail (low-traffic sites) | Low or Medium | Low |
| 10 <= Risk < 50 | Adware servers, rogue popup URLs | Low, Medium, or High | Low or Medium |
| Risk = 50 | Anonymizers, parked websites, unknown files | Medium or High | Medium |
| 50 < Risk < 80 | No proven legitimate activity observed | Low | High or Critical |
| 80 <= Risk < 100 | No proven legitimate activity, suspicious behavior | Medium | High or Critical |
| Risk = 100 | Known malicious resource, identified by a trusted vendor | High | High or Critical |
Risk Range is determined by combining:
-
Confidence - The threat intelligence teams certainty about the assessed severity level.
-
Severity - The inherent danger of the threat itself.
Higher Confidence and higher Severity generally result in higher Risk Ranges, calculated through a weighted scoring system.
Configuring and Managing Threat Prevention Policy
|
|
Note - The Threat Prevention policy runs only in prevent mode (blocks the detected threats). |
To create a Threat Prevention policy:
-
Access the Harmony SASE Administrator Portal and click Threat Prevention.
-
Click Add New Rule.
A new row appears in the table.
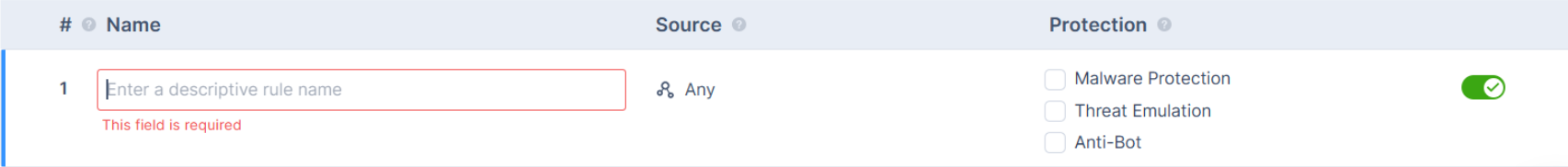
-
Specify these:
-
In the Name column, enter a descriptive name for the rule.
-
In the Source column, select to whom this rule should apply:
-
Any (default) - Applies to all resources.
-
Groups or Members - To add groups or members, hover over the source column and click Add Source.
The Manage Groups or Members window appears.
-
From the Groups section, select group(s).
-
From the Members section, select user(s).
-
Click Apply.
-
-
In the Protection column, select the types of protection this rule should provide:
-
Malware Protection
-
Threat Emulation
-
Anti-Bot
-
-
Turn on the toggle button, to enable the rule.
-
-
Click Apply.

-
The Apply Changes window appears.
-
Click Apply.
|
|
Notes:
|
Logs and Monitoring
-
All Threat Prevention events are sent to Infinity Events.
-
Each protection type (Malware Protection, Threat Emulation, and Anti-Bot) generates specific log entries.
-
Logs include details, such as risk score, action taken, and threat information.