Identity Agent for a User Endpoint Computer
This section describes how to configure an Identity Agent![]() Check Point dedicated client agent installed on Windows-based user endpoint computers. This Identity Agent acquires and reports identities to the Check Point Identity Awareness Security Gateway. The administrator configures the Identity Agents (not the end users). There are two types of Identity Agents - Full and Light. You can download the Full and Light Identity Agent package from the Captive Portal - 'https://<Gateway_IP_Address>/connect' or from sk134312. (a type of Identity Client) for a user endpoint computer.
Check Point dedicated client agent installed on Windows-based user endpoint computers. This Identity Agent acquires and reports identities to the Check Point Identity Awareness Security Gateway. The administrator configures the Identity Agents (not the end users). There are two types of Identity Agents - Full and Light. You can download the Full and Light Identity Agent package from the Captive Portal - 'https://<Gateway_IP_Address>/connect' or from sk134312. (a type of Identity Client) for a user endpoint computer.
Introduction
An administrator installs these Identity Agents on user endpoint computers that acquire and report user identities to the Identity Awareness![]() Check Point Software Blade on a Security Gateway that enforces network access and audits data based on network location, the identity of the user, and the identity of the computer. Acronym: IDA. Gateway.
Check Point Software Blade on a Security Gateway that enforces network access and audits data based on network location, the identity of the user, and the identity of the computer. Acronym: IDA. Gateway.
The administrator, not the users, configures these Identity Agents.
The Capabilities of Identity Agents
Types of Identity Agents for a User Endpoint Computer
|
|
Important - For more information, see sk134312. |
|
Type of Identity Agent |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Full |
This is a predefined client that includes packet tagging and computer authentication. The Windows administrator installs this client one time on a computer, and it applies to all users who log on to this computer. Windows administrator permissions are required to use the Full Identity Agent. The Full Identity Agent supports:
|
|
Light |
This is a predefined client that does not include packet tagging and computer authentication. The Windows administrator installs this client for each user who logs on to this computer. Windows administrator permissions are not required to use the Light Identity Agent. |
Comparison of the Light and Full Identity Agent Types
|
Category |
Item |
Full Identity Agent |
Light Identity Agent |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Installation Elements |
Installed component |
Application, Windows Service, Windows Driver |
Application only |
|
Required installation permissions |
Administrator |
None |
|
|
Required upgrade permissions |
None |
None |
|
|
Security Features |
User identification |
Single Sign-On |
Single Sign-On |
|
Computer identification |
Yes |
No |
|
|
Detection of an IP address change on the client computer |
Yes |
Yes |
|
|
Packet Tagging for Anti-Spoofing |
Yes |
No |
Downloading Identity Agents
It is a Best Practice to download the latest Identity Agents to endpoint computers from sk134312.
|
Identity Agent |
Path |
|---|---|
|
Full Identity Agent (Multi-User Host (MUH) Identity Agent |
Example for R81.10:
|
|
Light Identity Agent |
Example for R81.10:
|
An administrator of an Identity Awareness Gateway can require end users to download an Identity Agent from the Identity Awareness Captive Portal![]() A Check Point Identity Awareness web portal, to which users connect with their web browser to log in and authenticate, when using Browser-Based Authentication. so that they can access the Identity Awareness Gateway.
A Check Point Identity Awareness web portal, to which users connect with their web browser to log in and authenticate, when using Browser-Based Authentication. so that they can access the Identity Awareness Gateway.
-
Connect with SmartConsole to the Management Server
 Check Point Single-Domain Security Management Server or a Multi-Domain Security Management Server. that manages the Identity Awareness Gateway.
Check Point Single-Domain Security Management Server or a Multi-Domain Security Management Server. that manages the Identity Awareness Gateway. -
From the left navigation panel, click Gateways & Servers.
-
Open the Identity Awareness Gateway object.
-
From the left, click the Identity Awareness page.
-
Enable the Browser-Based Authentication and click Settings.
-
In the section Identity Agent Deployment from the Portal:
-
Select Require users to download.
-
Select the required Identity Agent type.
-
-
Click OK.
-
Install the Access Control Policy on the Identity Awareness Gateway.
By default, the version of the Identity Agent that end users download from the Identity Awareness Captive Portal is current to the General Availability release date of the Identity Awareness Gateway. Identity Agent is not updated in Jumbo Hotfix![]() Software package installed on top of the current software version to fix a wrong or undesired behavior, and to add a new behavior. Accumulators. An administrator can replace the default Identity Agent file on the Identity Awareness Gateway with a newer version of Identity Agent.
Software package installed on top of the current software version to fix a wrong or undesired behavior, and to add a new behavior. Accumulators. An administrator can replace the default Identity Agent file on the Identity Awareness Gateway with a newer version of Identity Agent.
-
Download the new version of Identity Agent from sk134312 to your computer.
-
Transfer the downloaded Identity Agent from your computer to the Identity Awareness Gateway to some directory (for example:
/var/log). -
Connect to the command line of the Identity Awareness Gateway.
-
Log in to the Expert mode.
-
Go to the required directory:
Copycd /opt/CPNacPortal/htdocs/nac/nacclients ; pwd -
Back up the current Identity Agent that you need to replace:
-
To back up the Full Identity Agent for Windows OS, run:
Copymv -v fullAgent.exe{,_BKP} -
To back up the Light Identity Agent for Windows OS, run:
Copymv -v lightAgent.exe{,_BKP} -
To back up the Custom Identity Agent for Windows OS, run:
Copymv -v customAgent.msi{,_BKP} -
To back up the Identity Agent for macOS, run:
Copymv -v Identity_Agent_Installer.dmg{,_BKP}
-
-
Move the new Identity Agent package to the required directory and give it the required name.

Note - In our example, we uploaded the Identity Agent package to the
/var/log/directory.-
To replace the Full Identity Agent for Windows OS, run:
Copymv -v /var/log/<File_Name>.exe /opt/CPNacPortal/htdocs/nac/nacclients/fullAgent.exe -
To replace the Light Identity Agent for Windows OS, run:
Copymv -v /var/log/<File_Name>.exe /opt/CPNacPortal/htdocs/nac/nacclients/lightAgent.exe -
To replace the Custom Identity Agent for Windows OS, run:
Copymv -v /var/log/<File_Name>.msi /opt/CPNacPortal/htdocs/nac/nacclients/customAgent.msiTo replace the Identity Agent for macOS, run:
Copymv -v /var/log/<File_Name>.dmg /opt/CPNacPortal/htdocs/nac/nacclients/Identity_Agent_Installer.dmg
-
-
Assign the required ownership to the new Identity Agents package:
Copychown -v admin:root /opt/CPNacPortal/htdocs/nac/nacclients/<File_Name>.<File_Extension> -
Assign the required permissions to the new Identity Agent package:
Copychmod -v 644 /opt/CPNacPortal/htdocs/nac/nacclients/<File_Name>.<File_Extension> -
Connect to the Captive Portal.
-
Make sure you can download thew new Identity Agent.
Authentication with an Identity Agent
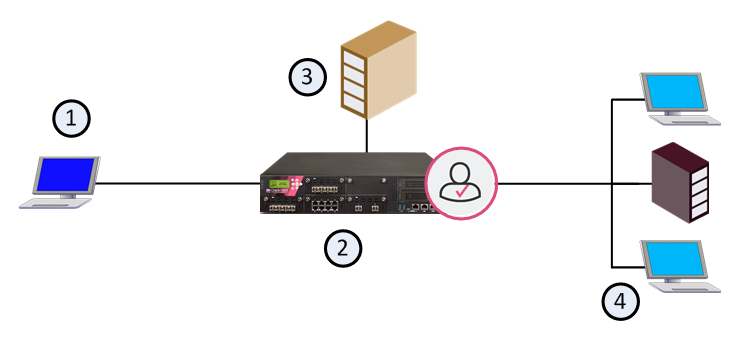
|
Item |
Description |
|---|---|
|
1 |
User that is trying to connect to the internal network |
|
2 |
Identity Awareness Gateway |
|
3 |
Active Directory domain controller |
|
4 |
Internal network |
High-level overview of the Identity Awareness authentication process
-
A user logs in to a computer with credentials and requests access to the Internal Data Center.
-
The Identity Agent connects to the Identity Awareness Gateway:
-
If the Identity Agent is already installed, then it connects to the Identity Awareness Gateway.
-
If the Identity Agent is not installed yet:
-
The Identity Awareness Gateway does not recognize the user and redirects the user to the Identity AwarenessCaptive Portal.
-
The user logs in to Captive Portal.
-
The Captive Portal shows a link to download the Identity Agent (if the Identity Awareness Gateway administrator configured so).
-
The user downloads the Identity Agent from the Captive Portal and installs it.
-
The Identity Agent connects to the Identity Awareness Gateway.
-

Note - If SSO with Kerberos is configured, the user is automatically connected.
-
-
The Identity Awareness Gateway authenticates the user.
-
The Identity Awareness Gateway sends the connection to its destination, based on the Access Control Policy.

