Introduction
Check Point and Aviatrix have partnered to deliver a best-in-class experience for customers that want to extend advanced security protections and drastically simplifying their multi-cloud network architecture.
Aviatrix cloud networking software delivers a single, common platform for multi-cloud networking, regardless of public cloud providers used. Aviatrix delivers the simplicity and automation enterprises expected in the cloud with the necessary visibility and control.
This document provides instructions about how to configure and deploy Check Point Firewalls from the Aviatrix Controller.
Prerequisites
-
Already configured Aviatrix Controller and Aviatrix Gateways
-
All Security Domains are defined in the Aviatrix Controller
-
Basic operation knowledge of Aviatrix and Check Point software
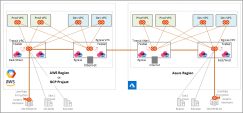
Architecture Overview
This section provides an overview of a standard design pattern for East-West, Ingress, and Egress traffic inspection with Check Point Security Gateways. To deploy a dedicated ingress zone, see the Check Point Cloud Security Blueprint 2.0.
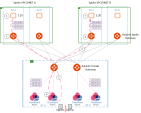
Example - East-West Packet Walk for AWS, Azure, and Google (GCP):
-
Aviatrix programs the local VPC/VNET route table that pointed to the Aviatrix Spoke Gateway.
-
Aviatrix Spoke Gateway sends traffic to one of the Aviatrix Transit Gateways.
-
Aviatrix Transit Gateway PBR rules to determine if either source or destination requires FireNet. If there is a match, then traffic is redirected to the one of the available CloudGuard Security Gateways.
-
CloudGuard processes the packet and sends the traffic back to the Aviatrix Transit Gateway.
-
Aviatrix Transit Gateway receives packet from the CloudGuard Security Gateway and sends the packer to the destination Aviatrix Spoke Gateway.
-
Aviatrix Spoke Gateway routes traffic to the VPC/VNET route table.
-
EC2/VM see this as an native VPC communication flow.
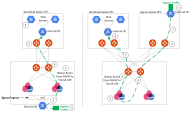
Context Aware Service Insertion
Ingress Traffic Flow
Ingress Designs and Packet Walk for AWS, Azure, and Google (GCP)