Overview of CloudGuard Network for Azure VMSS
Use this guide to:
-
Deploy a new Check Point VMSS for Microsoft Azure.
-
Configure an existing Check Point VMSS for Microsoft Azure
 Collection of integrated cloud services that developers and IT professionals use to build, deploy, and manage applications through a global network of data centers managed by Microsoft®., for templates 20180610 and above.
Collection of integrated cloud services that developers and IT professionals use to build, deploy, and manage applications through a global network of data centers managed by Microsoft®., for templates 20180610 and above.You can locate the template version on each CloudGuard instance in this file:
/etc/cloud-version
|
|
Note - For the list of supported versions, refer to the Support Life Cycle Policy. |
Licensing
Check Point CloudGuard Security Gateways and Check Point CloudGuard Security Management Server![]() Dedicated Check Point server that runs Check Point software to manage the objects and policies in a Check Point environment within a single management Domain. Synonym: Single-Domain Security Management Server. must have a license.
Dedicated Check Point server that runs Check Point software to manage the objects and policies in a Check Point environment within a single management Domain. Synonym: Single-Domain Security Management Server. must have a license.
There are two licensing options:
-
Pay As You Go (PAYG)
-
Bring Your Own License (BYOL)
Because the number of Security Gateways in VMSS can increase and decrease over time, we recommend that you use Security Gateways with the Pay As You Go (PAYG) license model. For the list of countries, see sk109360.
You can use the Check Point VMSS for Microsoft Azure solution template to launch BYOL Security Gateways.
To buy BYOL licenses, contact Check Point Sales.
For more information about licensing, see the CloudGuard Network Central License Management Utility guide.
|
|
Important - A VMSS with a mixture of BYOL and PAYG Security Gateways is not supported. All Security Gateways in a Scale Set must use the same payment plan, either PAYG or BYOL. |
Introduction to Virtual Machine Scale Sets (VMSS)
Virtual Machine Scale Sets (VMSS) are an Azure compute resource you can use to deploy and manage sets of identical Virtual Machines (VMs). The Scale Sets increase or decrease the number of Virtual Machines based on the current needs.
For example, multiple web servers server a web application. The web servers are deployed across multiple fault and update domains. A Load Balancer distributes network traffic across this group of web servers as needed.
In the current cyber-landscape, it is very important that you protect these environments from attackers with a security solution that is as scalable as the resources it protects. As the number of resources you protect scales up or down, the number of Security Gateways that provide protection has to scale as well.
Azure Autoscale is set up to increase or decrease the number of Check Point CloudGuard Network Security Gateways that protect your environment in the VMSS. A Check Point Security Management Server![]() Check Point Single-Domain Security Management Server or a Multi-Domain Security Management Server. manages these Security Gateways. The Security Management Server can be located either in Azure, or on-premises.
Check Point Single-Domain Security Management Server or a Multi-Domain Security Management Server. manages these Security Gateways. The Security Management Server can be located either in Azure, or on-premises.
See Azure documentation for information on the configuration of multiple Virtual Machines - Configure multiple virtual machines in an availability set for redundancy.
Prerequisites
Make sure you are familiar with these topics:
|
Vendor |
Topics |
|---|---|
|
Microsoft Azure |
|
|
Check Point |
|
Components of the Check Point Deployed Solution
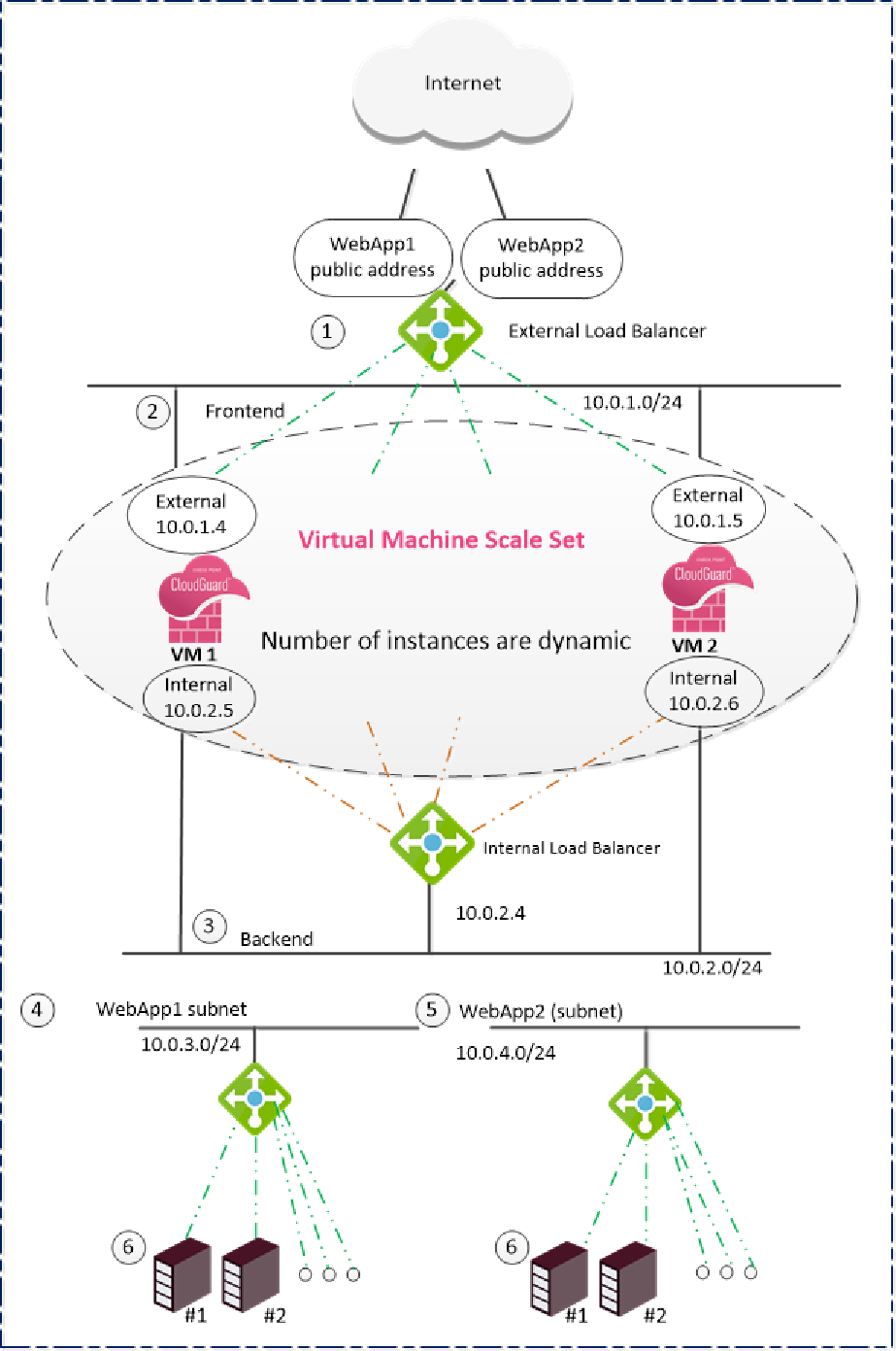
The diagram below depicts an Azure Virtual Network![]() Environment of logically connected Virtual Machines. (VNET) with the Check Point solution deployed.
Environment of logically connected Virtual Machines. (VNET) with the Check Point solution deployed.
There are two backend subnets - WebApp1 and WebApp2.
WebApp1 and WebApp2 are each a user-deployed backend subnet. Each has its own load-balanced web server.
The Check Point deployed solution has these components:
-
Frontend subnet
-
Virtual Machine Scale Set (VMSS)
The number of instances that you can deploy in the Cloud is dynamic.
-
Internal Load Balancer
-
Backend subnet
-
External Load Balancer
-
Public IP address for each VMSS instance (optional)
-
You cannot deploy other VMs in the VMSS subnets