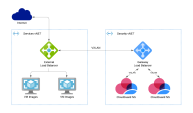
Network-Diagram
Traffic flow explanation
Inbound:
-
The External Load Balancer redirects all packets to the Gateway Load Balancer.
VXLAN tunnel preserves the original source and destination addresses.
-
The Gateway Load Balancer send packet to next healthy CloudGuard Gateway
 Check Point Virtual Security Gateway that protects dynamic virtual environments with policy enforcement. CloudGuard Gateway inspects traffic between Virtual Machines to enforce security, without changing the Virtual Network topology..
Check Point Virtual Security Gateway that protects dynamic virtual environments with policy enforcement. CloudGuard Gateway inspects traffic between Virtual Machines to enforce security, without changing the Virtual Network topology.. -
CloudGuard Gateway decides if to forward or drop packet.
-
External Gateway Load Balancer sends the inspected packet to next VM in the Backend Pool.
-
External Load Balancer redirects reply packets to the Gateway Load Balancer.
-
Symmetrical hashing return packet to the original CloudGuard Gateway to keep state.
-
External Load Balancer sends return packet to original source address.
When inbound traffic arrives, the CloudGuard Gateway receives it follows:
-
A VXLAN tunneled traffic with:
-
Source: The Gateway Load Balancer frontend IP.
-
Service: UDP services with the VXLAN tunnel interfaces port numbers (internal & external).
-
Destination: The VMSS instance.
-
-
Encapsulated traffic with:
-
Source: Original source.
-
Service: Original service.
-
Destination: Original (The Frontend IP of the External Load Balancer).
-
|
|
Note - Traffic flow is the same for Load Balancing rule |
Outbound:
-
The External Load Balancer receives traffic from a Backend Pool VM.
The External Load Balancer redirects all packets to the Gateway Load Balancer.
VXLAN tunnel preserves the original source and destination addresses.
-
Gateway Load Balancer sends packet to next healthy CloudGuard Gateway.
-
CloudGuard Gateway decides forward or drop packet.
-
External Load Balancer sends request packet to original destination address.
-
External Load Balancer redirects reply packet to Gateway Load Balancer.
-
Symmetrical hashing return packet to original CloudGuard Gateway to keep state.
-
External Gateway Load Balancer sends inspected reply packet to original source address, a Backend Pool VM.
When outbound traffic arrives, the CloudGuard Gateway receives it follows:
-
A VXLAN tunneled traffic with:
-
Source: The Gateway Load Balancer frontend IP.
-
Service: UDP services with the VXLAN tunnel interfaces port numbers (internal & external).
-
Destination: The VMSS instance.
-
-
Encapsulated traffic with:
-
Source: Original source (The Frontend IP of the External Load Balancer).
-
Service: Original service.
-
Destination: Original destination.
-
Gateway Load Balancer Frontend Routing Table - User Defined Routes (UDR):
| Name | Destination | Nexthop |
|---|---|---|
|
Local-Subnet |
Gateway Load Balancer Frontend subnet |
Virtual network |
|
To-VNet |
Gateway Load Balancer VNet: |
None (drop) |