Splitting the Ports with Breakout Cables
Breakout Cables
Quantum Maestro Orchestrators![]() A scalable Network Security System that connects multiple Check Point Security Appliances into a unified system. Synonyms: Orchestrator, Quantum Maestro Orchestrator, Maestro Hyperscale Orchestrator. Acronym: MHO. have 100 / 40 GbE ports.
A scalable Network Security System that connects multiple Check Point Security Appliances into a unified system. Synonyms: Orchestrator, Quantum Maestro Orchestrator, Maestro Hyperscale Orchestrator. Acronym: MHO. have 100 / 40 GbE ports.
With a breakout cable![]() An optical fiber cable that contains several jacketed simplex optical fibers that are packaged together inside an outer jacket. Synonyms: Fanout cable, Fan-Out cable, Splitter cable., it is possible to split the supported 100 / 40 GbE port into four 10 GbE ports.
An optical fiber cable that contains several jacketed simplex optical fibers that are packaged together inside an outer jacket. Synonyms: Fanout cable, Fan-Out cable, Splitter cable., it is possible to split the supported 100 / 40 GbE port into four 10 GbE ports.
Insert the splitter cables to convert each applicable QSFP28 100 GbE port into four SFP28 10 GbE ports.
|
|
Important - The breakout cable that splits 100 GbE port into four 25 GbE ports is not supported. |
Example of a breakout cable:
MHO-175 Splitting Options
It is possible to split each of the QSFP28 ports 1 to 32 (colored green) into four SFP28 ports.
In MHO-175, all port LEDs are located on the right side.
There are 32 LEDs that correspond to the 32 physical ports.
You can connect 1-to-4 breakout cables to physical ports and get a maximum of 128 logical ports.
After you connect a breakout cable to a physical port, you get four additional interfaces starting from the original interface name. You assign these interfaces to Security Groups![]() A logical group of Security Appliances that provides Active/Active cluster functionality. A Security Group can contain one or more Security Appliances. Security Groups work separately and independently from each other. To the production networks, a Security Group appears a single Security Gateway. Every Security Group contains: (A) Applicable Uplink ports, to which your production networks are connected; (B) Security Appliances (the Quantum Maestro Orchestrator determines the applicable Downlink ports automatically); (C) Applicable management port, to which the Check Point Management Server is connected..
A logical group of Security Appliances that provides Active/Active cluster functionality. A Security Group can contain one or more Security Appliances. Security Groups work separately and independently from each other. To the production networks, a Security Group appears a single Security Gateway. Every Security Group contains: (A) Applicable Uplink ports, to which your production networks are connected; (B) Security Appliances (the Quantum Maestro Orchestrator determines the applicable Downlink ports automatically); (C) Applicable management port, to which the Check Point Management Server is connected..
Example - When you connect a breakout cable to the top port 8 (interface "eth1-29"), you get:
|
Port |
Interface |
Port |
|---|---|---|
|
8 |
eth1-29 |
Port 1/8/1 |
|
eth1-30 |
Port 1/8/2 |
|
|
eth1-31 |
Port 1/8/3 |
|
|
eth1-32 |
Port 1/8/4 |
|
|
Note - For more information about the ports and interface names in Gaia, see Quantum Maestro Orchestrator Ports and Gaia OS Interfaces. |
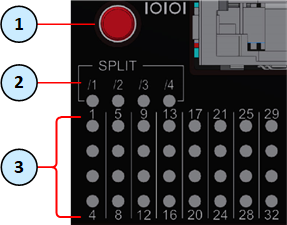
To see the state of split ports, it is necessary to use the control button to select the LED indication mode.
The control button (item 1) selects one of the five available LED indication modes in a cycle.
The four LEDs in the section SPLIT /1 /2 /3 /4 (item 2) show the current LED indication mode.
The port LEDs (item 3) show the port state - link (up or down) and traffic (flowing or not).
|
|
Important:
|
MHO-170 Splitting Options
It is possible to split only the top QSFP28 odd ports 1 to 29 (colored green) into four SFP28 ports, each.
When the top odd ports 1 to 29 (colored green) are in split mode, the corresponding bottom QSFP28 even ports 2 to 30 are disabled (colored red).
|
|
Important - It is not supported to connect a breakout cable to Port 31 because it disables the dedicated synchronization Port 32. |
After you connect breakout cables to the top ports, you get four additional interfaces starting from the original interface name. You assign these interfaces to Security Groups.
Example - When you connect a breakout cable to the top port 15 (interface "eth1-29"), you get:
|
Port |
Interface |
Port |
|---|---|---|
|
15 |
eth1-29 |
Port 1/15/1 |
|
eth1-30 |
Port 1/15/2 |
|
|
eth1-31 |
Port 1/15/3 |
|
|
eth1-32 |
Port 1/15/4 |
|
|
Note - For more information about the ports and interface names in Gaia, see Quantum Maestro Orchestrator Ports and Gaia OS Interfaces. |
MHO-140 Splitting Options
It is possible to split only the top QSFP28 ports 49, 51, 53, and 55 (colored green) into four SFP28 ports, each.
When the top ports (colored green) are in a split mode, the corresponding bottom QSFP28 ports 50, 52, 54, and 56 are disabled (colored red).
After you connect breakout cables to the supported top ports, you get four additional interfaces starting from the original interface name. You assign these interfaces to Security Groups.
Example - When you connect a breakout cable to the top port 49 (eth1-49), you get:
|
Port |
Interface |
Port |
|---|---|---|
|
49 |
eth1-49 |
Port 1/49/1 |
|
eth1-50 |
Port 1/49/2 |
|
|
eth1-51 |
Port 1/49/3 |
|
|
eth1-52 |
Port 1/49/4 |
|
|
Note - For more information about the ports and interface names in Gaia, see Quantum Maestro Orchestrator Ports and Gaia OS Interfaces. |